|
edit SideBar
|
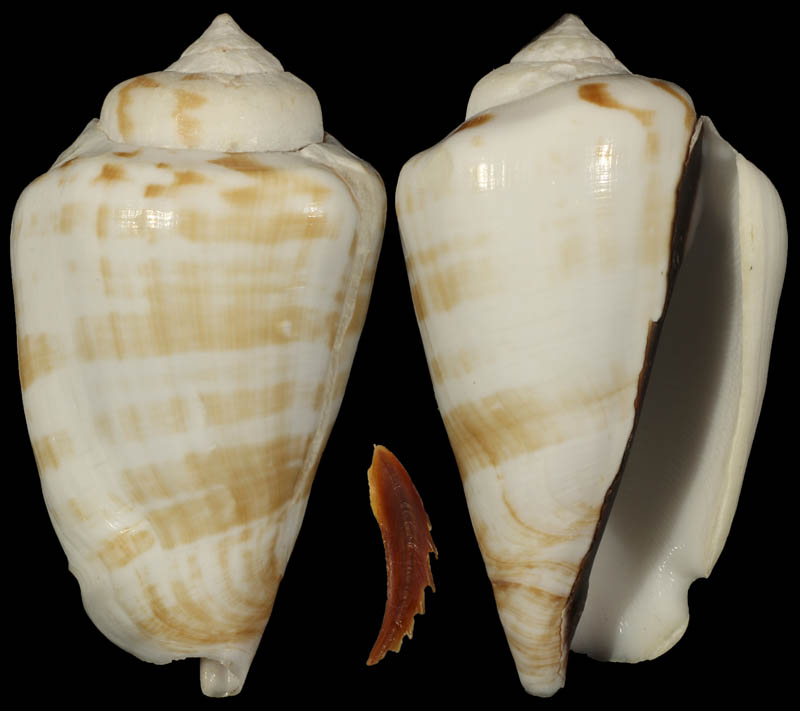
Species / Conomurex Luhuanus
Stromboidea
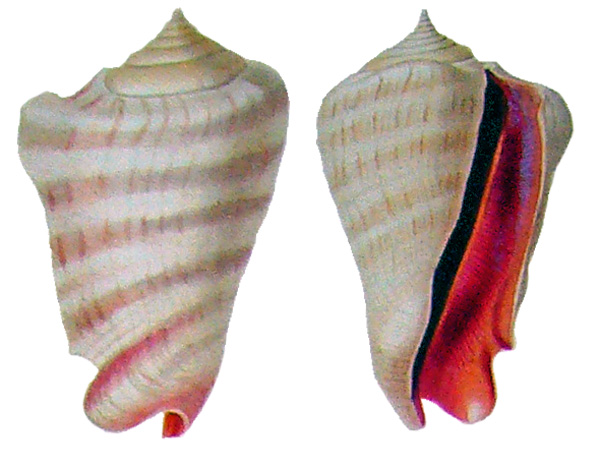
Original Description of Strombus Luhuanus by Linnaeus, 1758, p. 744:
- "S. testae labro prominulo, dorso laevi, anfractibus rotundatis aequalibus."
Locus typicus: "Habitat in O. Asiae frequens."
Linnaeus cited:
- Rumph. mus. t. 37. f. S.
- Argenv. conch. t. 17. f. N.
History and Synonymy
Conomurex luhuanus (Linnaeus, 1758: 744) (Strombus)
- Syn.: Strombus linea nigra Scopoli in Volta, 1787:237
- Syn.: Strombus luguanus Herbst, 1788: 203, pl. 48 fig. 2 [?err. pro. luhuanus]
- ? Syn.: Strombus pusillus Anton, 1839: 86 [fide Abbott, 1960, a juvenile specimen not recognisable from description; nomen inquirendum]
1742
in Argenville, 1742, pl. 17, fig. N
in Gualthieri, 1742, pl. XXXI, fig. H
in Gualthieri, 1742, pl. XXXI, fig. I
1766
Luhuana in Rumphius, 1766, pl. XXXVII, fig. S
1787
Description of Strombus linea nigra by Scopoli in Volta, 1787, p. 237:
- "Strombus linea nigra Scop. testa ex albo, & luteo maculata; labio exteriore tenui: interiore linea fusca longitudinali. Spec. 7. Gualt. Tab. XXXI. fig. H."
1842
Strombus luhuanus in Sowerby, 1842, pl. VII, fig. 54
Strombus luhuanus in Gray, 1842, pl. 2, fig. 6
1843
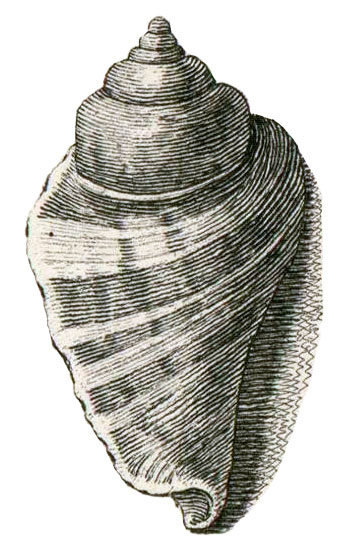
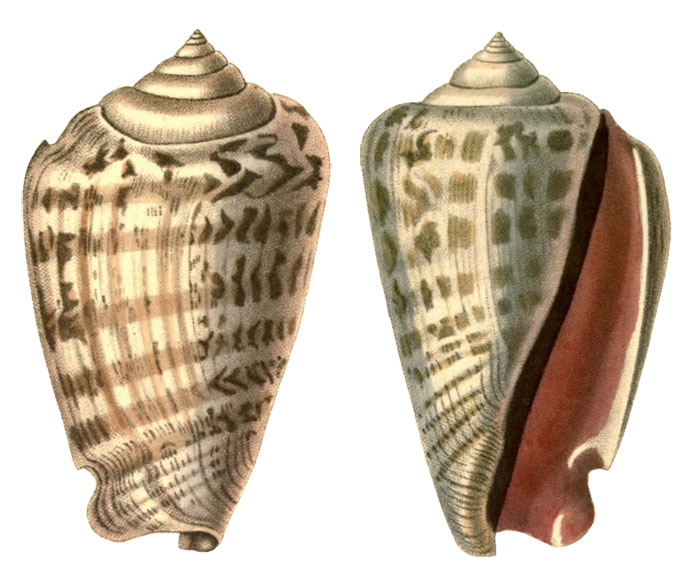
Strombus luhuanus in Kiener, 1843, Vol. 4, Strombus pl. 27, fig. 1;
"Image courtesy Biodiversity Heritage Library. http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org"
1844
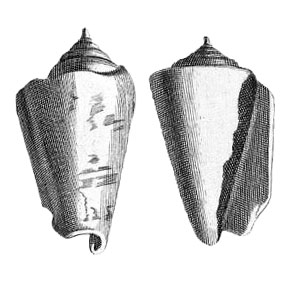
Strombus luhuanus in Duclos, 1844, pl. 14, fig. 2
Strombus luhuanus in Duclos, 1844, pl. 16, fig. 1, 2
1850
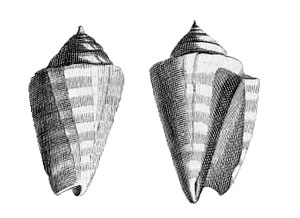
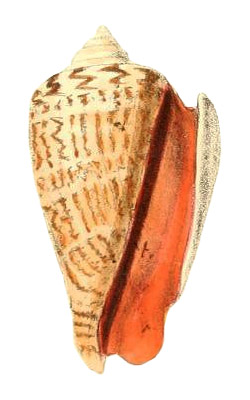
Strombus luhuanus in Reeve, 1850, Strombus, pl. 9, fig. 19
1972
Strombus (Conomurex) luhuanus in Ladd, 1972, pl. 19, fig. 2
2017
Sanchez-Escalona, K.P., Aliño, P.A., Juinio-Meñez, Ma.A. 2017:
- Abstract: "Sexual size dimorphism of Strombus luhuanus was explored with Geometric Morphometries. Using 39 landmarks and semi-landmarks, principal component analysis (PCA) showed possible separation of sexes with significant loadings on shoulder and the inner lip. Discriminant Function Analysis (DFA) cross-validated classification showed males and females can be identified using the generated shape variables with 83.72% and 71.43% accuracy respectively. Examination of the generated mean shape showed that males are slimmer while females are more bulbous with vector changes along the inner lip and shoulder. Sexual shape may be related to differential energy allocation of reproduction with males spending more on finding a mate and females devoting more on egg production. Statistically quantified shape dimorphism will facilitate better understanding of reproductive behaviour and natural population dynamics of this species."
Reports
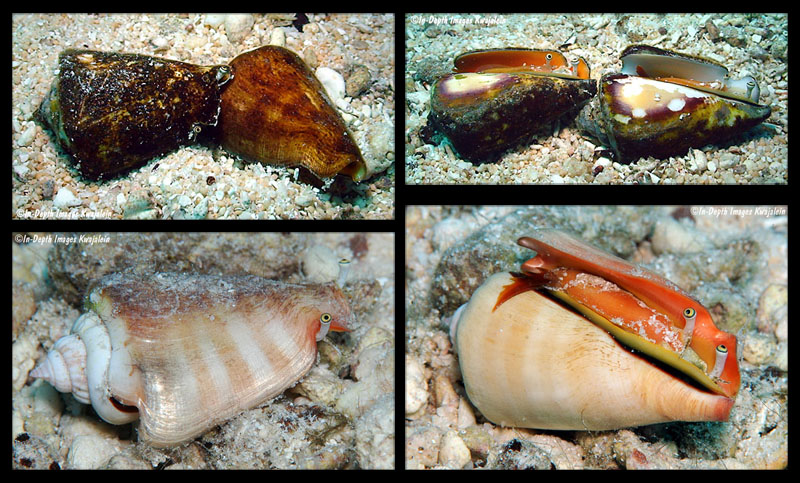
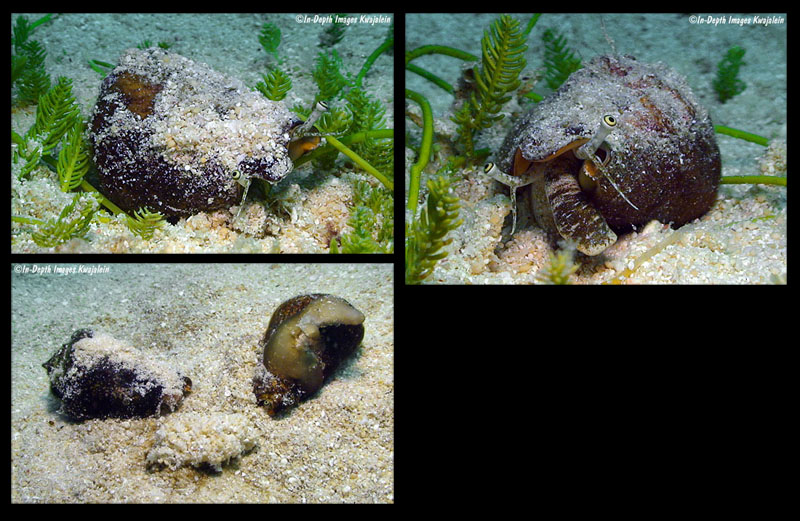
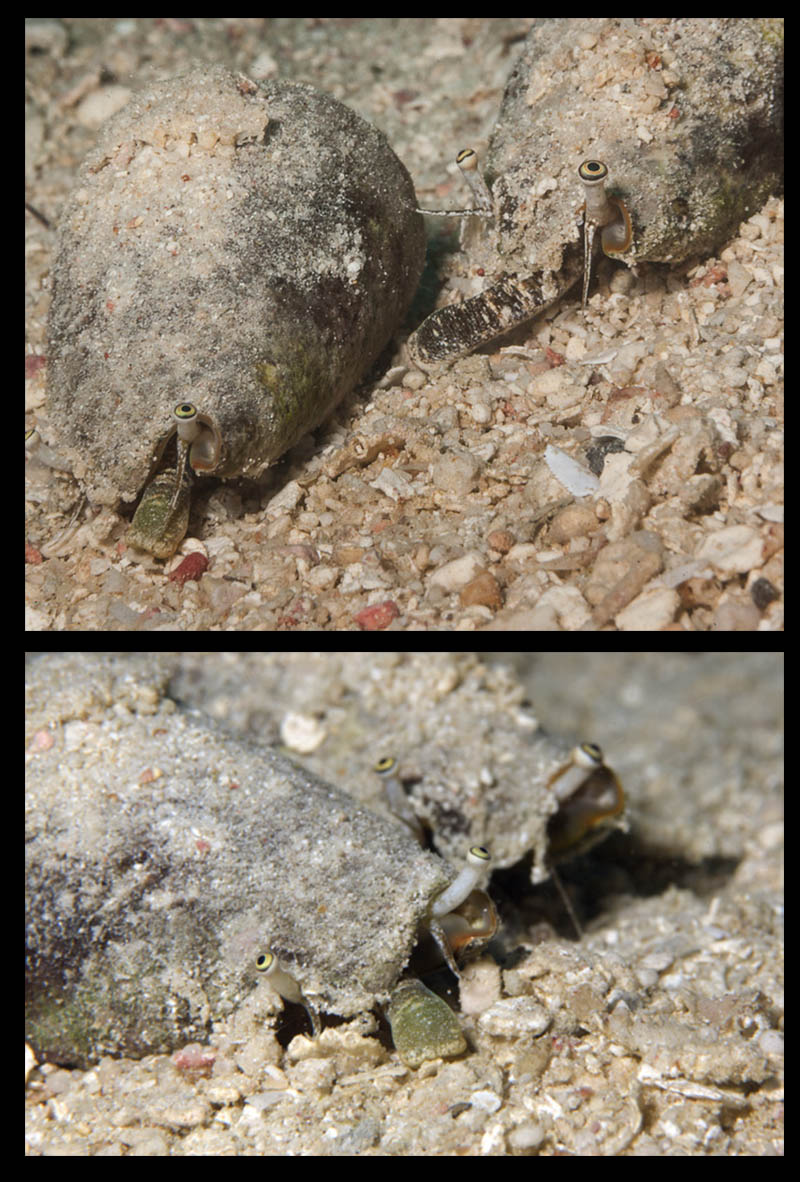
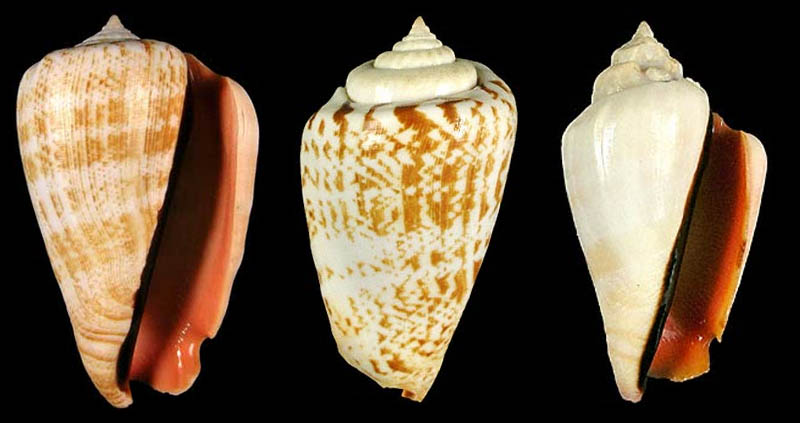
Jeanette & Scott Johnson about Conomurex luhuanus from Kwajalein Atoll:
- "Conomurex luhuanus are abundant within Marshall Islands lagoons, but are rarely found on the seaward reefs. Specimens can be found in large numbers on many shallow sand and rubble lagoon interisland reefs as well as on pinnacles at depths from about 1 to at least 16m. Sizes range up to about 60mm. Most specimens have an orange-red aperture, hence the common name (Blood mouth conch). A few, however have apertures either yellow or pure white.
- top: "Both orange and white aperture specimens"
- bottom: "Closer shot of a relatively clean-shelled individual. The underside shows the orange red aperture."
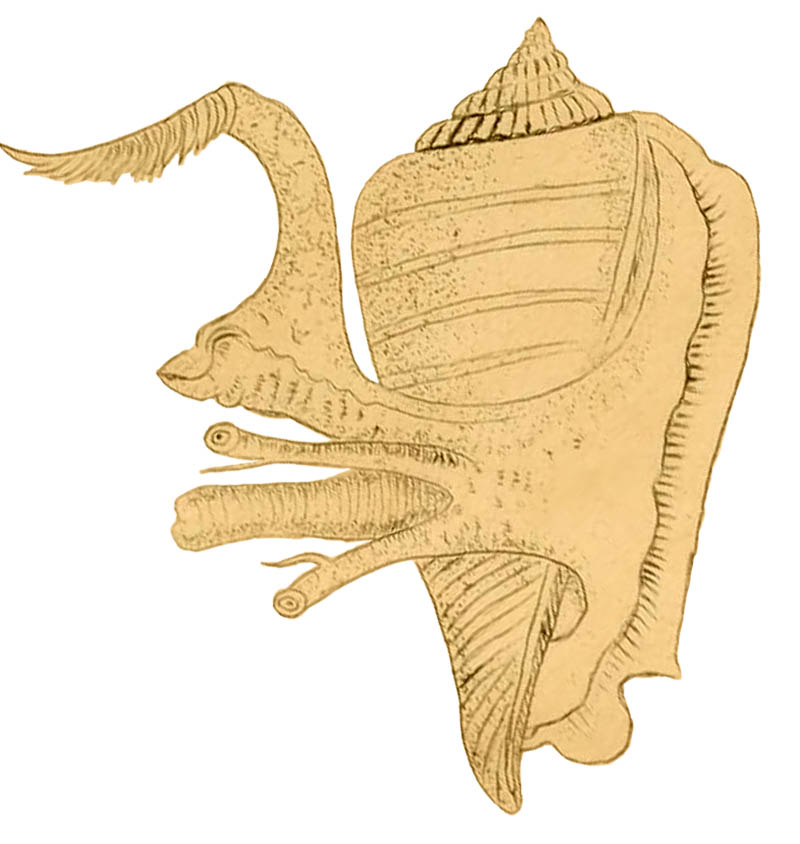
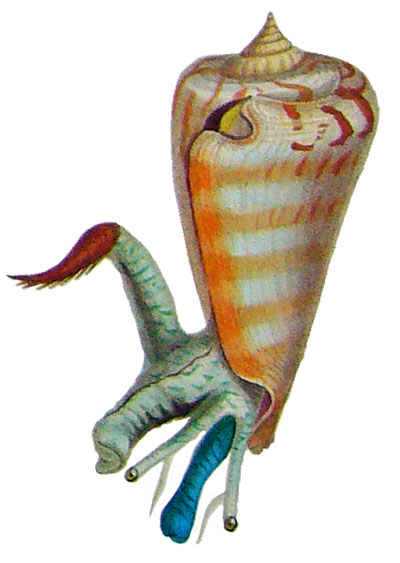
- top: "Like other Strombidae, it has a long proboscis for feeding on algae."
- bottom: "A pair of algae and sand encrusted individuals with an egg mass, mixed in with that clump of sand in front of the two shells."
All Photos of Kwajalein Atoll-specimens courtesy Scott & Jeanette Johnson, Kwajalein Atoll
Bob Abela on Conomurex luhuanus from Guam
Conomurex luhuanus (Linnaeus, 1758); ~20 ft. A pair singled out among a large colony; Outhouse Beach, Apra Harbor, Guam; 03 Jan 2007; photo Bob Abela
Amy-Rose Saunders from Queensland
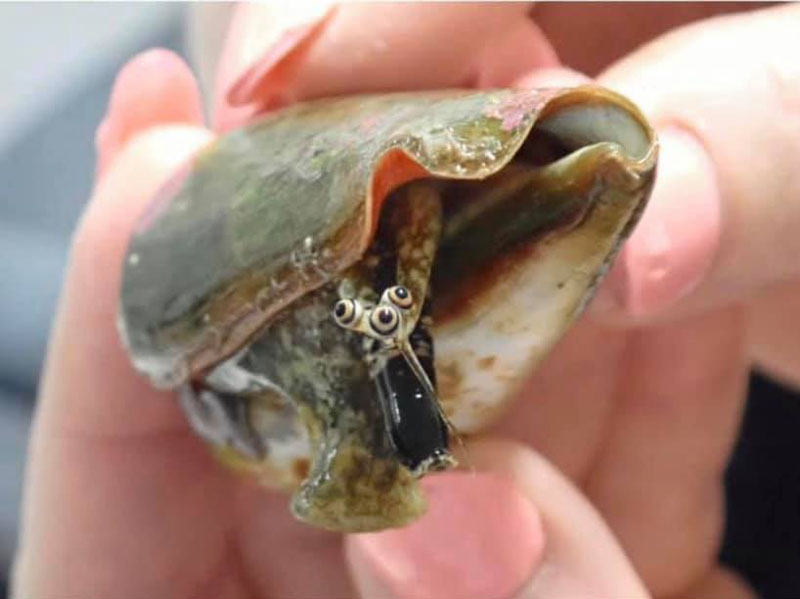
Conomurex luhuanus with three eyes; GBR area, Queensland, Australia; living in a tank in Ultra Coral Australia Company, photo by Gemma Lucy Moore
Monika & Francesco Giovanoli
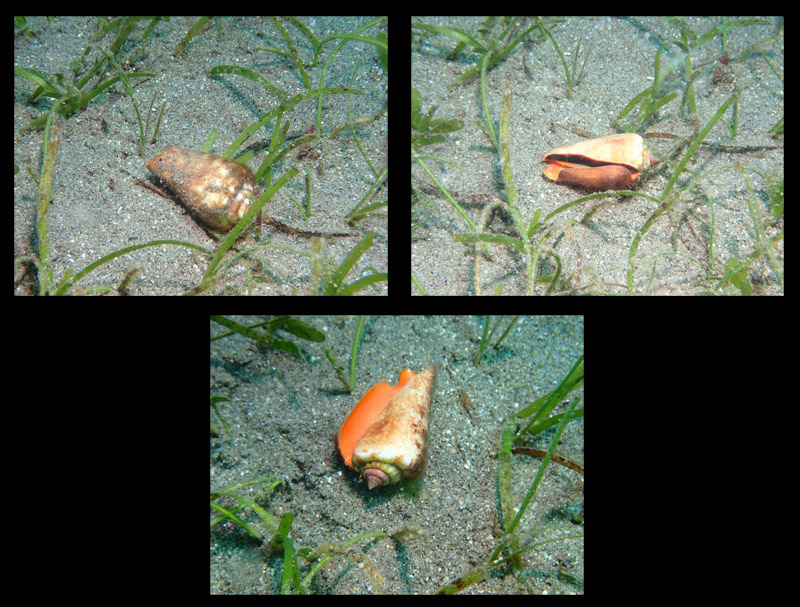
Conomurex luhuanus (Linnaeus, 1758); Dauin, Visayas, Philippines; dived at 5m, 28.06.2023, and their habitat; Photos Francesco & Monika Giovanoli
Specimens from private collections
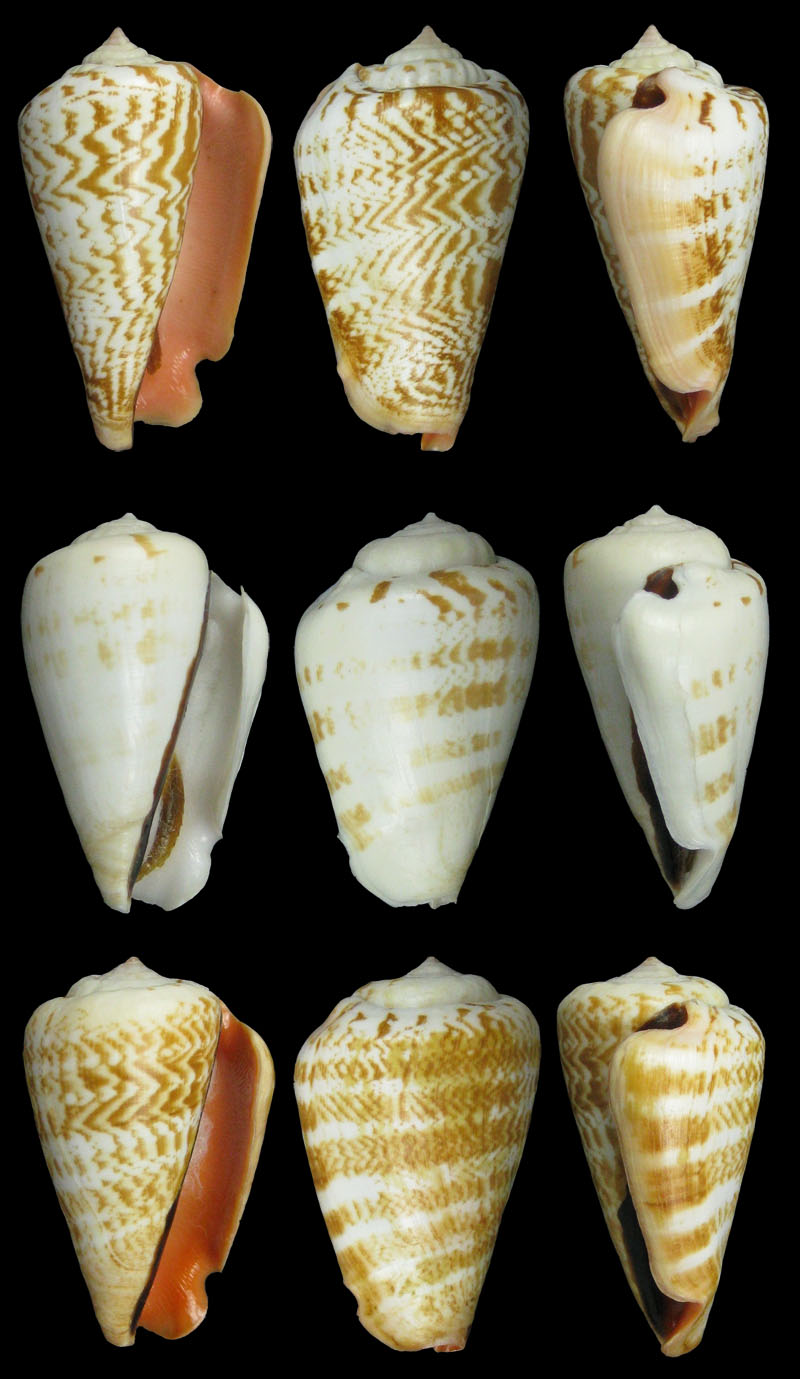
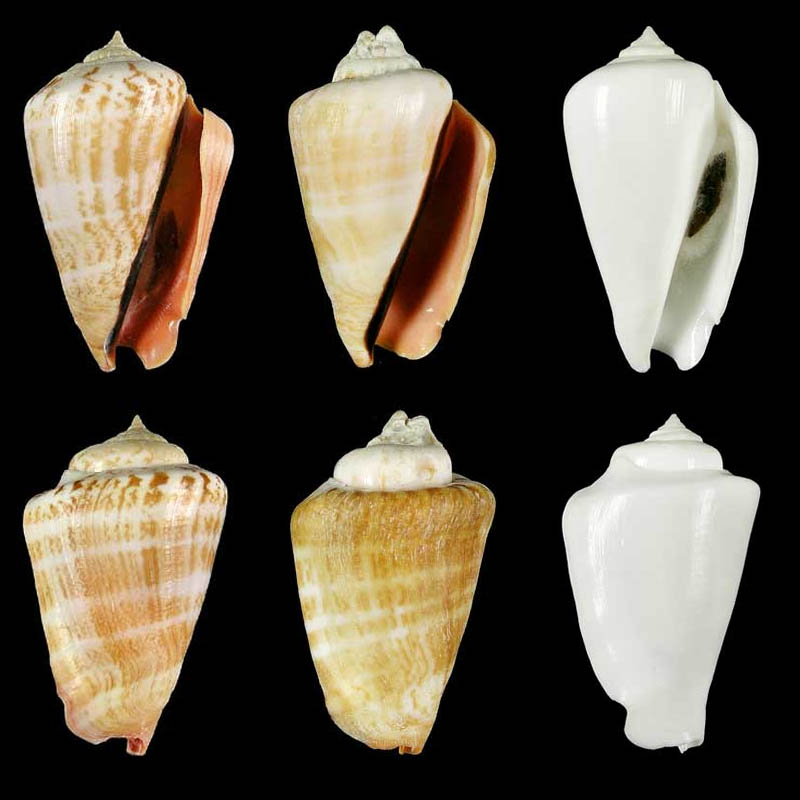
Conomurex luhuanus (Linnaeus, 1758); Crash Boat Basin, Apra Harbor, Guam Island, Mariana Islands, Micronesia, USA, North Pacific Ocean; On reef, 15 feet, Scuba; 4/1978; 1: 48,9 mm, 2: 49,7 mm, 3: 42,9 mm, 4: 39,2 mm, 5: 41,5 mm; Coll. Richard Salisbury
Conomurex luhuanus (Linnaeus, 1758); Apra Harbor, Guam Island, Mariana Islands, Micronesia, USA, North Pacific Ocean; 10-15 ft on reef; Coll. Paul Merrill
- t: 40 mm, Freak, pink lip, 1980
- m: 50,3 mm, pink lip, 1983
- b: 56,2 mm, pink lip, 1985
Conomurex luhuanus (Linnaeus, 1758); Apra Harbor, Guam Island, Mariana Islands, Micronesia, USA, North Pacific Ocean; 10-15 ft on reef; 1985; Coll. Paul Merrill
- t: 57 mm, pink lip
- m: 53 mm, white lip
- b: 53 mm, orange lip
Conomurex luhuanus (Linnaeus, 1758); yellow lip; Apra Harbor, Guam Island, Mariana Islands, Micronesia, USA, North Pacific Ocean; 10-15 ft on reef; 1985; 50,0 mm; Coll. Paul Merrill
Conomurex luhuanus (Linnaeus, 1758); Apra Harbor, Guam Island, Mariana Islands, Micronesia, USA, North Pacific Ocean; 10-15 ft on reef; 1985; 50,1 mm; Coll. Paul Merrill
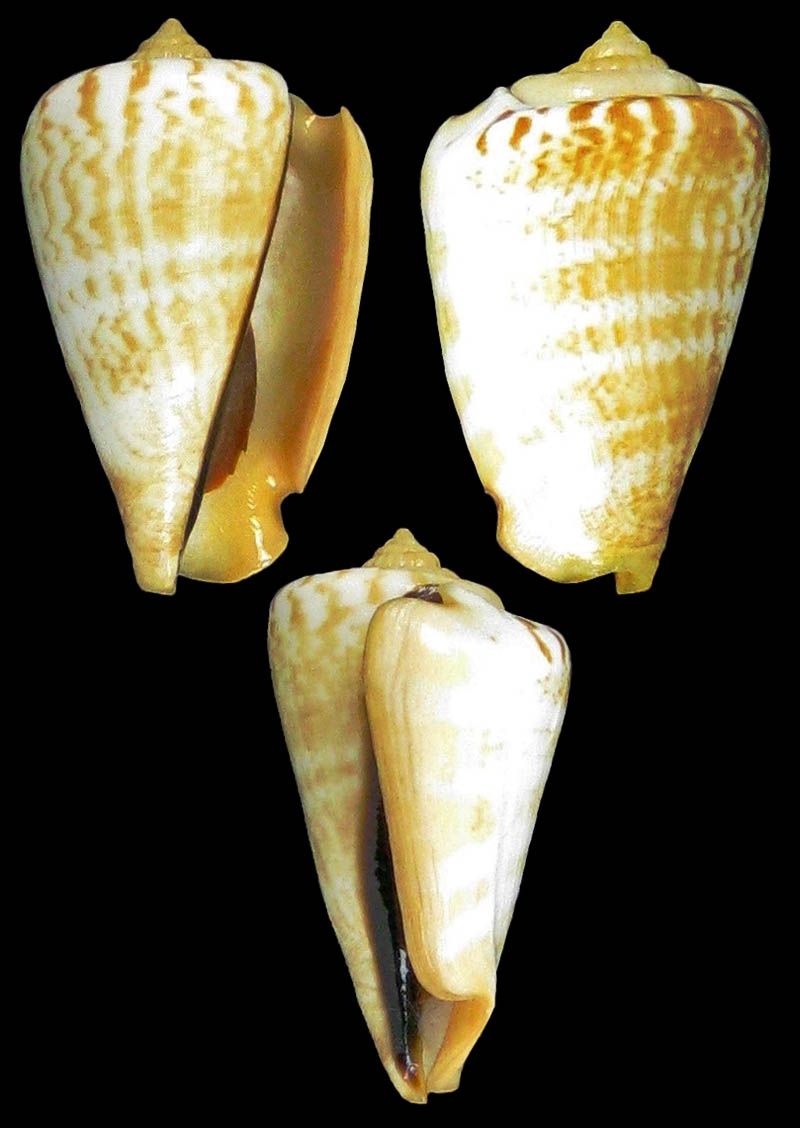
Conomurex luhuanus (Linnaeus, 1758); Australia; Coll. Guido Poppe
- Western Australia, off Port Hedland; from fisherman; 1990; 52,8 mm; no. 109915
- Western Australia, off Port Hedland; from fisherman; 1990; 55,3 mm; no. 109921
- Western Australia, off Port Hedland; from fisherman; 1990; 57,8 mm; no. 109916
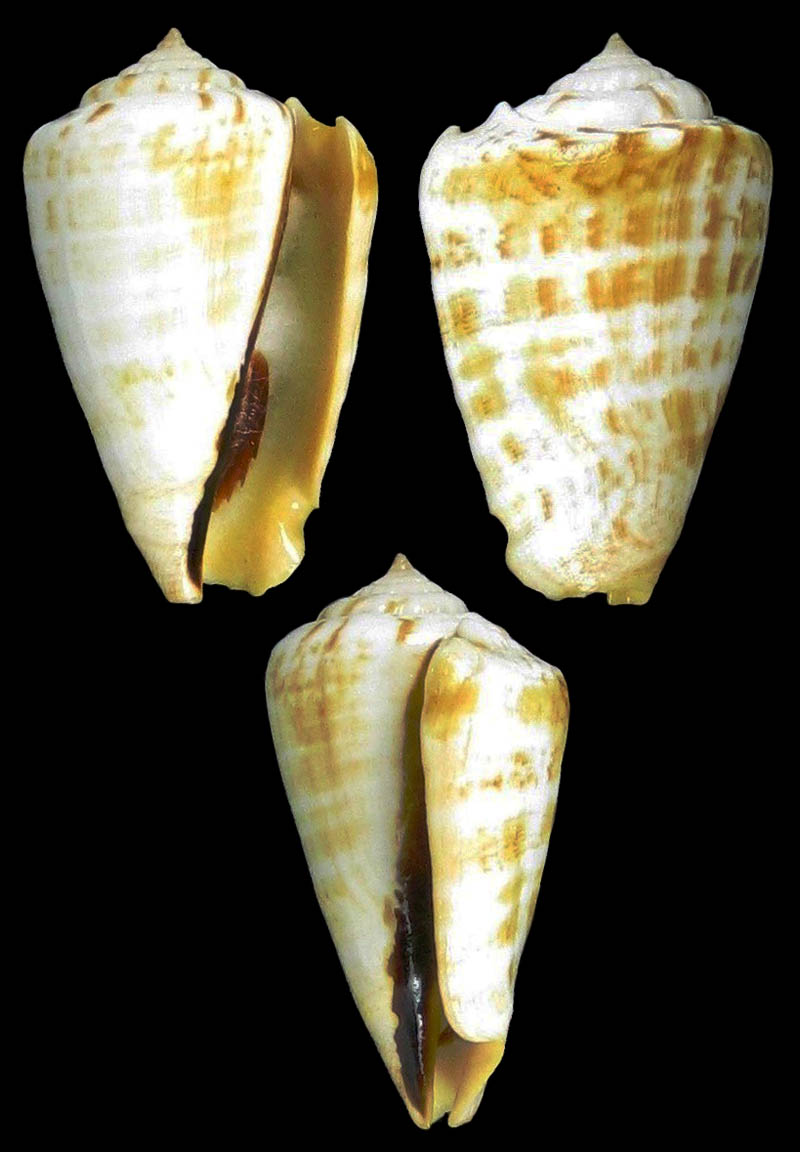
Conomurex luhuanus (Linnaeus, 1758); Coll. Guido Poppe
- l: Dingo Beach, Queensland State, north east Australia; found in rubble on reef at low tide; 4/1990; 52 mm; Ex-coll. D. & M. Meyer; Coll. Guido Poppe no. 345373
- m: Fananu Island, Truk Dist, E. Carolines; 59,8 mm; no. 125791
- r: off Tugela, KwaZulu-Natal Province, South Africa; on mud trawled; 11/1983; 39 mm; Ex-coll. D. & M. Meyer; coll. Guido Poppe no. 149322; Comment G. Poppe: "totally out of range-no one knows why"
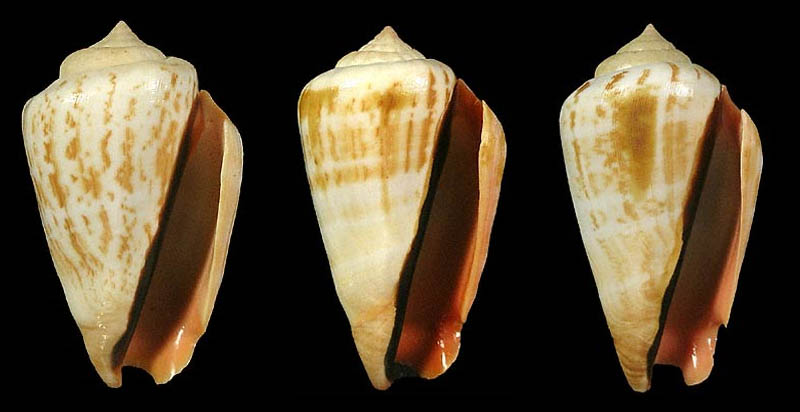
Conomurex luhuanus (Linnaeus, 1758); Coll. Guido Poppe
- l: Honiara, Guadalcanal Island, Guadalcanal Province, Solomon Islands, south-western Pacific; 1984; 60,5 mm; Ex-coll. Philippe Martin; Coll. Guido Poppe no. 236576
- m: off Tugela, KwaZulu-Natal Province, South Africa; on mud trawled; 11/1983; 40,7 mm; Ex-coll. D. & M. Meyer; Coll. Guido Poppe no. 346034
- r: albino; Laminusa Island, Sulu Archipelago, Sulu Province, A.R.M.M. Region; collected 10-15 meters deep by local fishermen; 2010; 55,4 mm; no. 568384
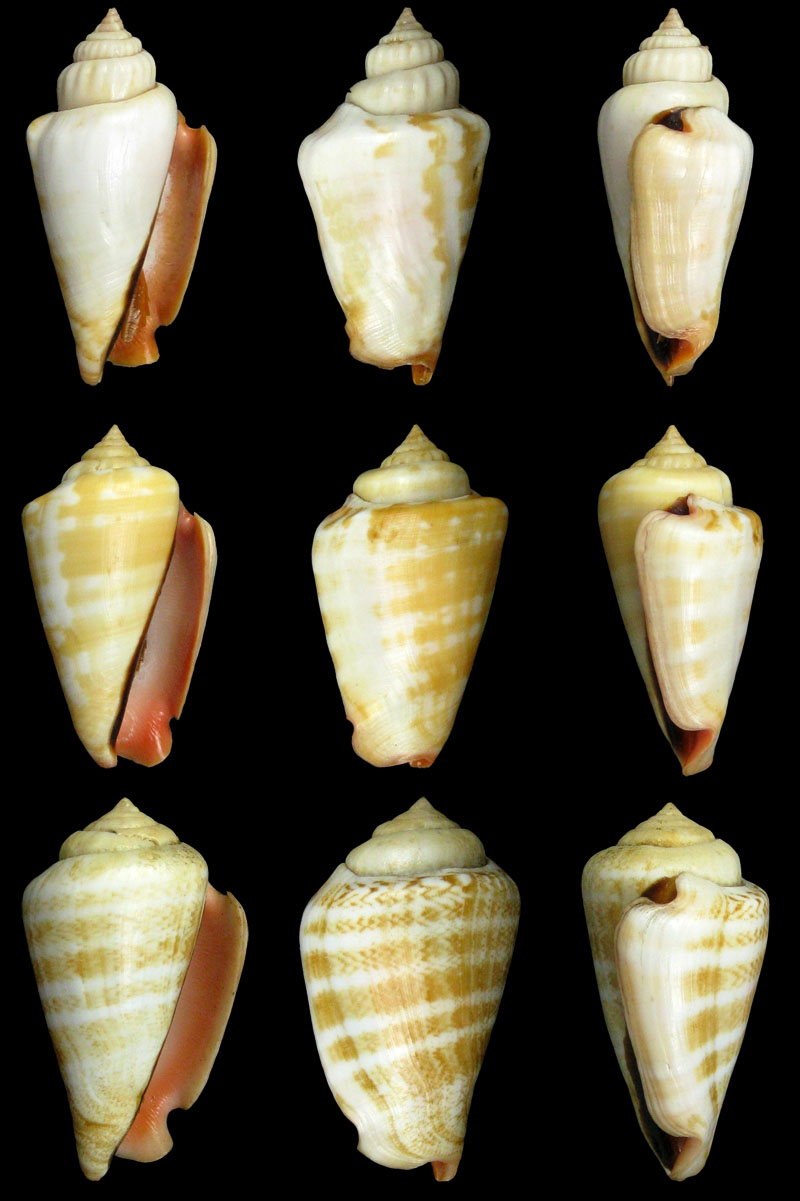
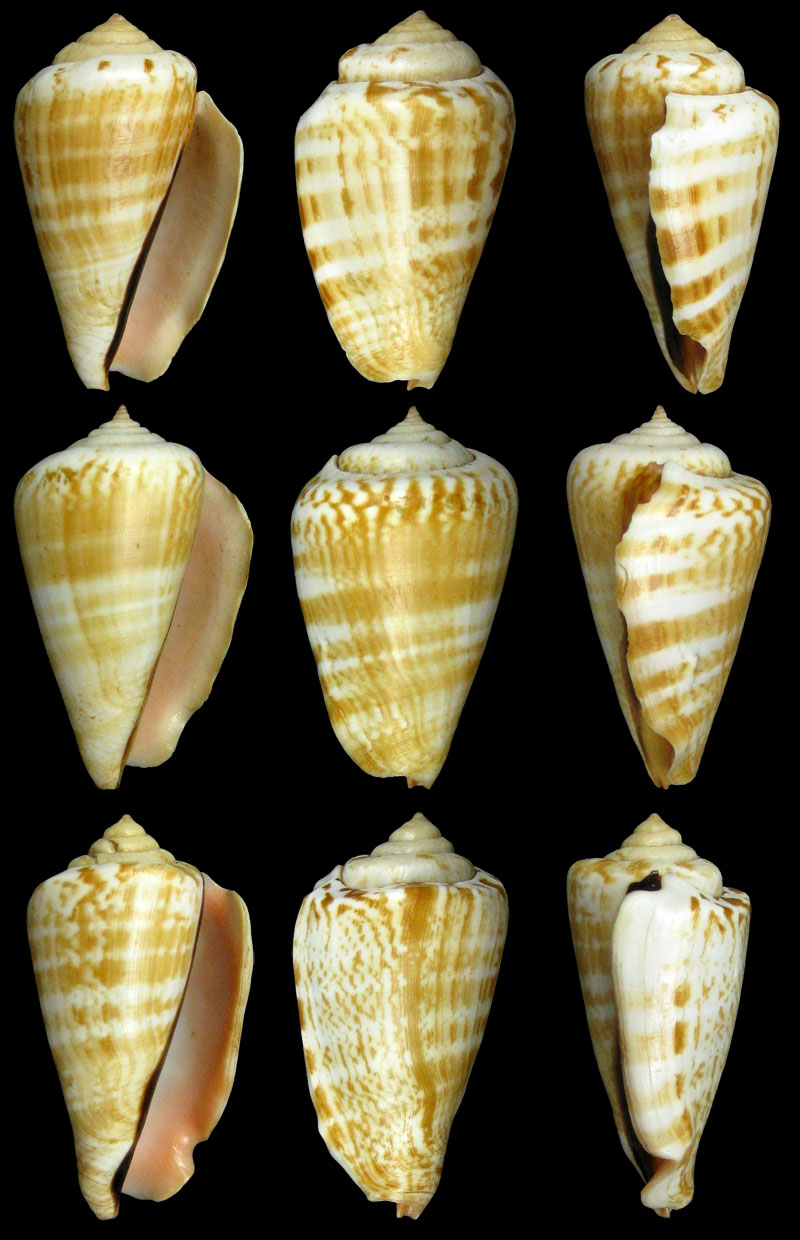
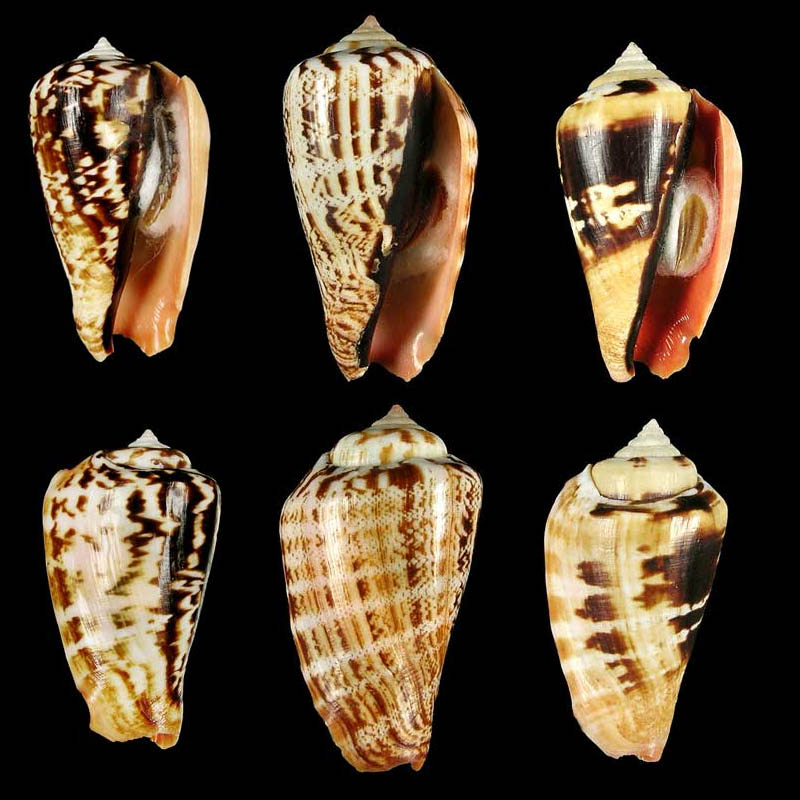
Conomurex luhuanus (Linnaeus, 1758); white lip, with periostracum; Philippines Islands; Coll. Guido Poppe
- l: Masbate Island, Masbate Province, Bicol Region; collected from local fishermen; 2006; 56,6 mm; no. 316287
- m: Masbate Island, Masbate Province, Bicol Region; collected from local fishermen; 2006; 56,3 mm; no. 320363
- r: Olango Island, Cebu Province, Central Visayas Region; 10-25 m; 2012; 48,5 mm; no. 725793
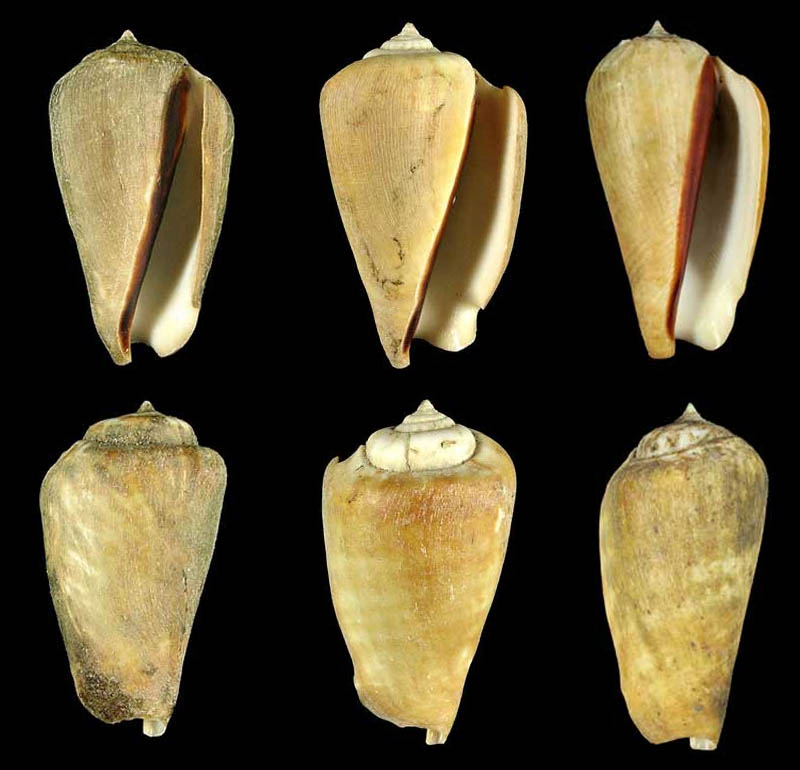
Conomurex luhuanus (Linnaeus, 1758); Wreck Beach, Sattihip, Thailand; 15-25 ft in rubble on sand; 1975; t: 48,5 mm; m: 55,1 mm, b: 52,1 mm; Coll. Paul Merrill
Conomurex luhuanus (Linnaeus, 1758); (subfossil?); Krabi Province, Thailand, Andaman Sea; 2001; Coll. René Vanwalleghem
- 59 mm
- 50 mm
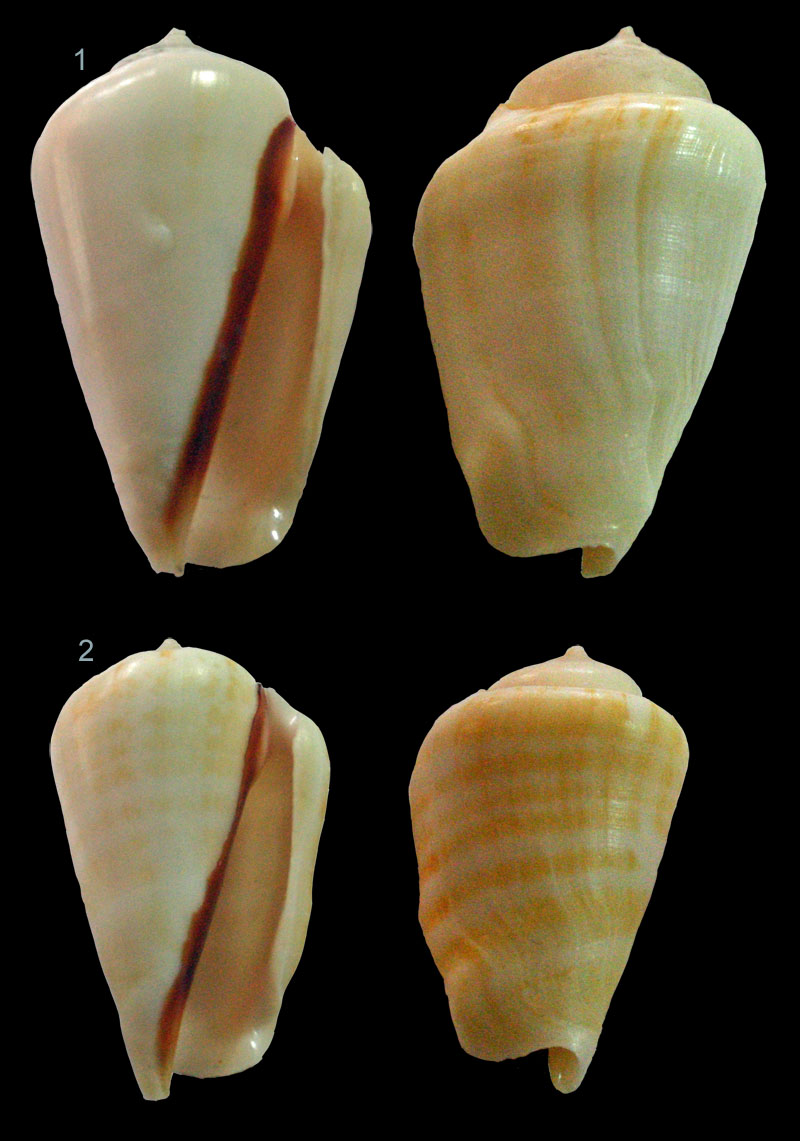
Conomurex luhuanus (Linnaeus, 1758); Japan Islands; 70 mm; Coll. Melinda Gaspar
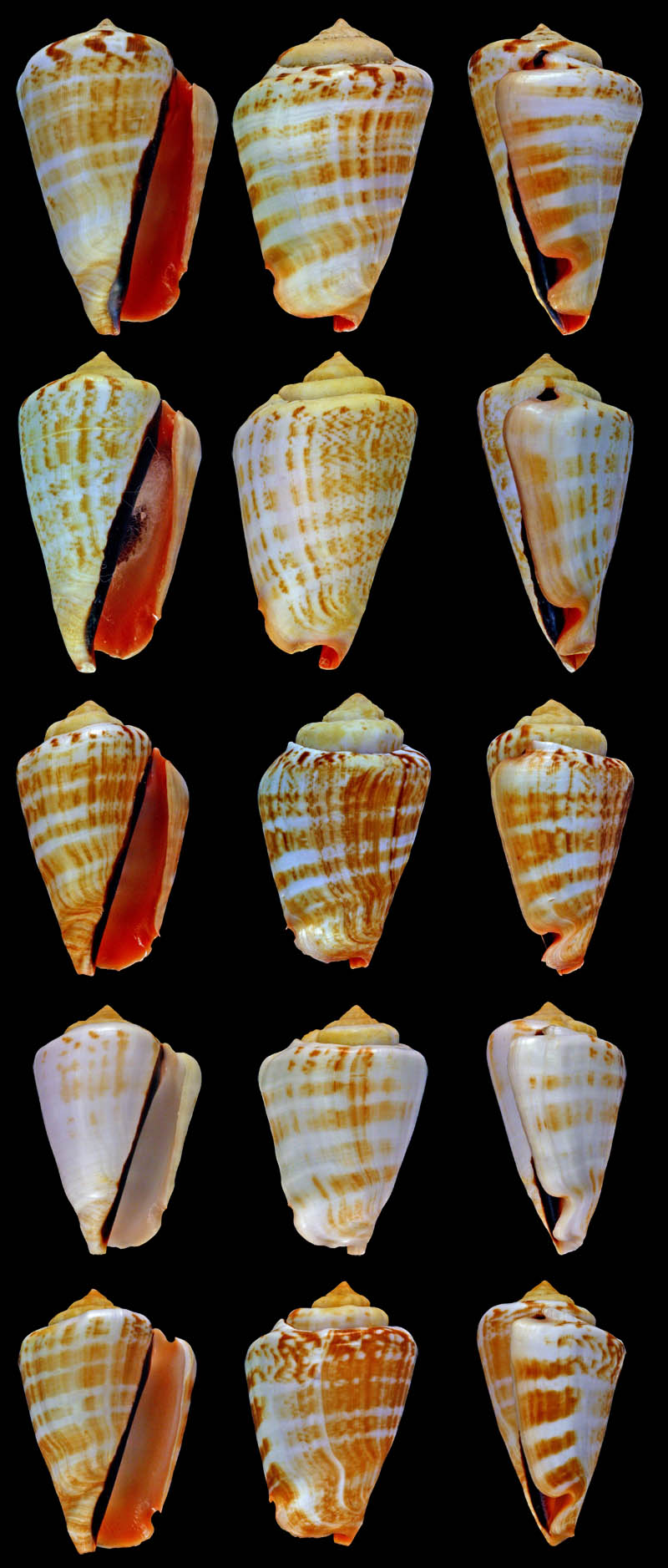
Conomurex luhuanus (Linnaeus, 1758); rare colour variations; Philippines Islands; Coll. Guido Poppe
- l: Zamboanga, Mindanao Island, Zamboanga Peninsula Region; 10-20 m; 2011; 51,8 mm; no. 632254
- m: Masbate Island, Masbate Province, Bicol Region; collected from local fishermen; 2006; 57,4 mm; no. 316564
- r: Masbate Island, Masbate Province, Bicol Region; from local fisherman; 2006; 48,0 mm; no. 363433
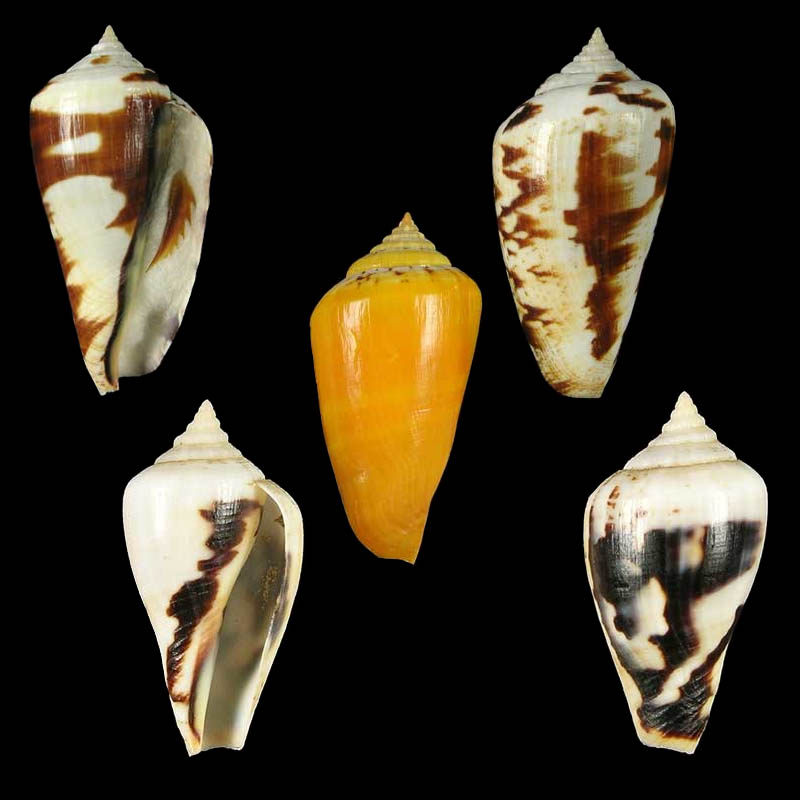
Conomurex luhuanus (Linnaeus, 1758); juvenile; rare colour variations; Philippines Islands; coll. Guido Poppe
- t: Bohol Island, Bohol Province, Central Visayas Region; dived 20-35 m; collected by local fishermen; 2009; the young shell, looks like Conus, lip not formed as yet; 41,6 mm; no. 517539
- m: Olango Island, Cebu Province, Central Visayas Region; 10-25 m; shells live and thrive on sand bottoms with a good mixture of mud, which covers them entirely. Sometimes already collected at a depth of 3 meters, but much more common between 12 and 20 m; 2012; 51,4 mm; no. 681298
- b: Zamboanga, Mindanao Island, Zamboanga Peninsula Region; 10-25 m; collected by local fishermen; 2009; 24,3 mm; no. 534176
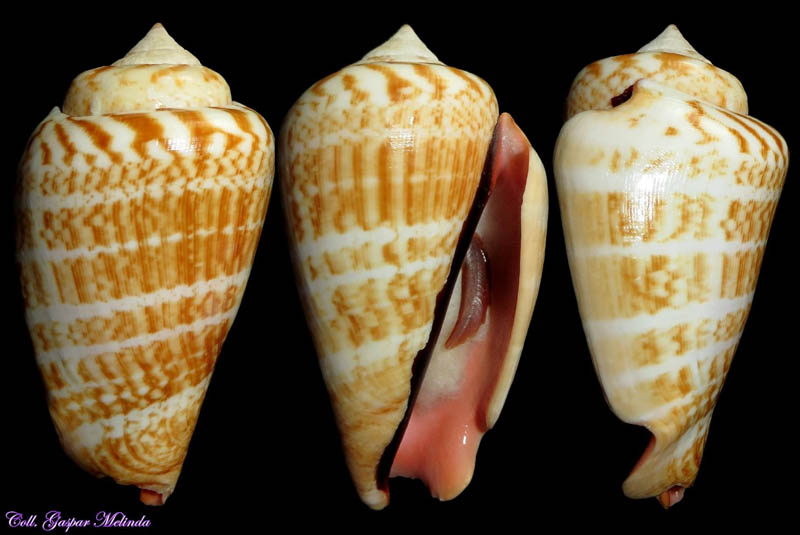
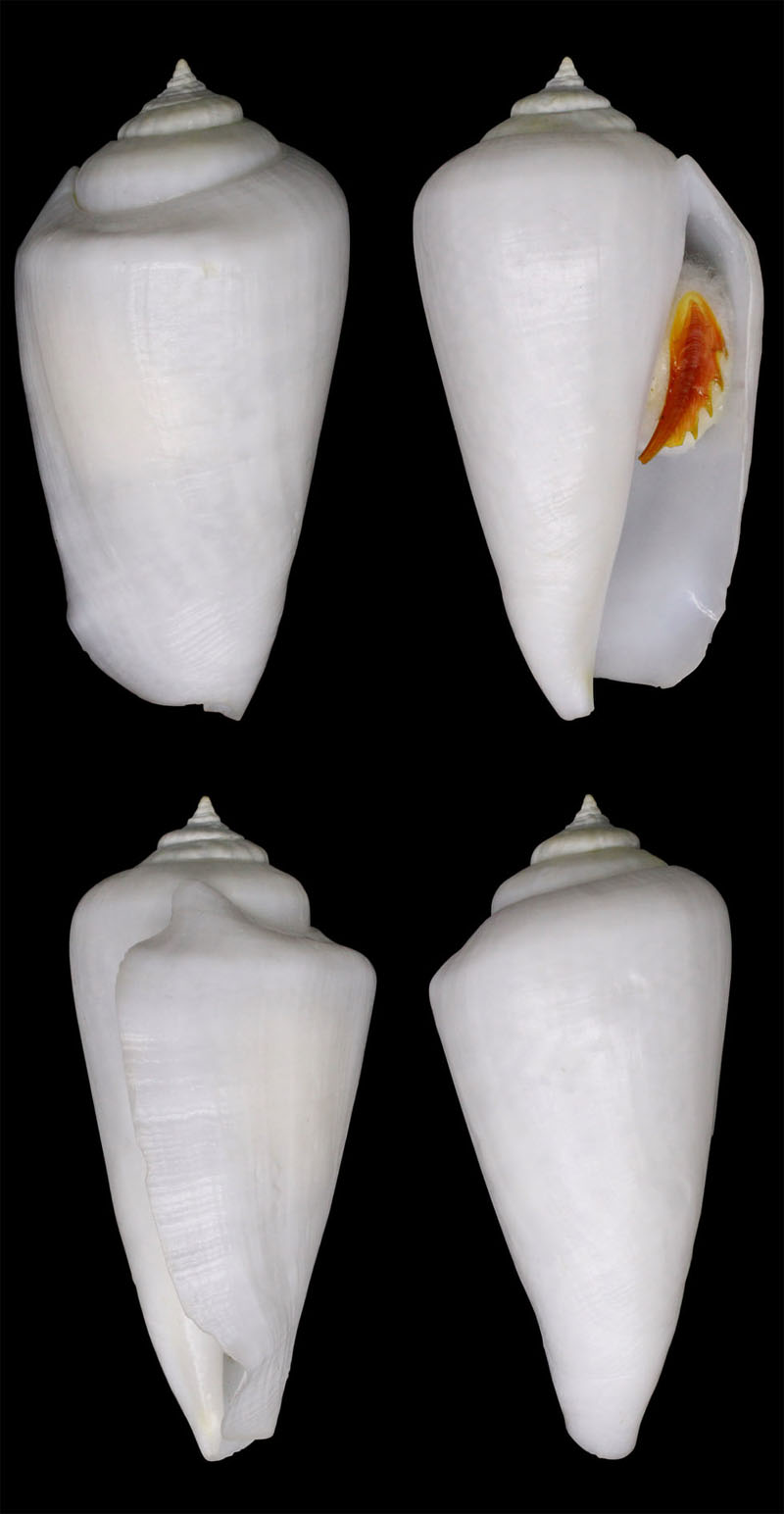
Conomurex luhuanus (Linnaeus, 1758), albino; Cebu Island, Philippines; 51,6 mm; Coll. Jean-Pierre Barbier
Conomurex luhuanus (Linnaeus, 1758); Cebu, Philippines; 55,4 mm; Coll. Goran Vertriest
Conomurex luhuanus (Linnaeus, 1758); Cebu, Philippines; 49,4 mm, pearl 5,7 mm; Coll. Goran Vertriest
Reports
- Doug Brennan: "I have seen large groups of S. luhuanus here (Mariana Islands, Saipan), on Guam, and in Okinawa."
References
- Adams, A. (1863). On the Species of Rostriferous Gasteropods (Strombidæ, Trichotropidæ, Cypræidæ, and Amphiperasidæ) found in Japan. Journal of the Proceedings of the Linnean Society of London. Zoology, 7(26), 91-96.
- Aliño, P. M., McManus, L. T., McManus, J. W., Nañola Jr, C. L., Fortes, M. D., Trono Jr, G. C., & Jacinto, G. S. (1993). Initial parameter estimations of a coral reef flat ecosystem in Bolinao, Pangasinan, northwestern Philippines. In Trophic models of aquatic ecosystems. ICLARM Conf. Proc (Vol. 26, pp. 252-258).
- Asigau, W. (1988). Strombus luhuanus L. 1758 (Gastropoda: Mollusca) on the reefs near Gabagaba Village, Papua New Guinea. Science in New Guinea, 14(1), 40-46.
- Baldwin, J. (1981). ON THE FUNCTIONS OF OCTOPINE DEHYDROGENASE AND ALANOPINE DEHYDROGENASE IN THE PEDAL RETRACTOR MUSCLE OF THE GASTROPOD MOLLUSK STROMBUS-LUHUANUS. In PROCEEDINGS OF THE AUSTRALIAN BIOCHEMICAL SOCIETY (Vol. 14, pp. 63-63). MONASH UNIV DEPT BIOCHEMISTRY, CLAYTON VICTORIA 3168, AUSTRALIA: PROC AUST BIOCHEMICAL SOC, p. 63
- Baldwin, J. (1982). An immunochemical study of structural and evolutionary relationships among molluscan octopine dehydrogenases.
- Baldwin, J., & England, W. R. (1982). Multiple forms of octopine dehydrogenase in Strombus luhuanus (Mollusca, Gastropoda, Strombidae): Genetic basis of polymorphism, properties of the enzymes, and relationship between the octopine dehydrogenase phenotype and the accumulation of anaerobic end products during exercise. Biochemical genetics, 20(9-10), 1015-1025.
- Baldwin, J., & England, W. R. (1982). The Properties and Functions of Alanopine Dehydogenase and Octopine Dehydrogenase from the Pedal Retractor Muscle of Strombidae (Class Gastropoda).
- Bellchambers, L. M., Meeuwig, J. J., Evans, S. N., & Legendre, P. (2011). Modelling habitat associations of the common spider conch in the Cocos (Keeling) Islands. Mar Ecol Prog Ser, 432, 83-90.
- Berg Jr, C. J. (1974). A comparative ethological study of strombid gastropods. Behaviour, 274-322.
- Bird, R. B., & Bird, D. W. (1995). Children and traditional subsistence on Mer (Murray Island), Torres Strait. Australian Aboriginal Studies, (1), 2.
- Blumer, M. J. (1995). The ciliary photoreceptor in the teleplanic veliger larvae of Smaragdia sp. and Strombus sp.(Mollusca, Gastropoda). Zoomorphology, 115(2), 73-81.
- Burley, D. V., & Connaughton, S. P. (2007). First Lapita Settlement and its Chronology in Vavau, Kingdom of Tonga. Radiocarbon, 49(1), 131-137.
- Carter, M. (2001). New evidence for the earliest human occupation in Torres Strait, northeastern Australia. Australian Archaeology, 50-52.
- Carter, M., Veth, P., Barham, A., Bird, D., O’Connor, S., & Bird, R. (2004). Archaeology of the Murray Islands, eastern Torres Strait: Implications for a regional prehistory. Woven Histories Dancing Lives: Torres Strait Islander Identity, Culture and History, 234-258.
- Catterall, C. P., & Poiner, I. R. (1983). Age-and sex-dependent patterns of aggregation in the tropical gastropod Strombus luhuanus. Marine Biology, 77(2), 171-182.
- Catterall, C. P., & Poiner, I. R. (1987). The potential impact of human gathering on shellfish populations, with reference to some NE Australian intertidal flats. Oikos, 114-122.
- Catterall, C. P., Poiner, I. R., & O'Brien, C. J. (2001). Long‐term population dynamics of a coral reef gastropod and responses to disturbance. Austral Ecology, 26(6), 604-617.
- Chapman, H. F. (1983). Uptake and Depuration of Petroleum Hydrocarbons by a Tropical Marine Gastropod Strombus Luhuanus (Doctoral dissertation, School of Australian Environmental Science, Griffith University).
- Chapman, H. F., & Connell, D. W. (1986). Uptake and clearance of diesel alkanes from sediments by the Great Barrier Reef gastropod Strombus luhuanus. Marine Biology, 92(1), 15-19.
- Chardy, P., Chevillon, C., & Clavier, J. (1988). Major benthic communities of the south-west lagoon of New Caledonia. Coral Reefs, 7(2), 69-75.
- Clark, G., & Reepmeyer, C. (2012). Last millennium climate change in the occupation and abandonment of Palau's Rock Islands. Archaeology in Oceania, 47(1), 29-38.
- Dolorosa, R. G., & Jontila, J. B. S. (2013). Notes on common macrobenthic reef invertebrates of Tubbataha Reefs Natural Park, Philippines. Science Diliman, 24(2).
- Doney, S. C., Fabry, V. J., Feely, R. A., & Kleypas, J. A. (2009). Ocean acidification: the other CO2 problem. Marine Science, 1.
- Duda Jr, T. F., & Kohn, A. J. (2005). Species-level phylogeography and evolutionary history of the hyperdiverse marine gastropod genus< i> Conus</i>. Molecular phylogenetics and evolution, 34(2), 257-272.
- Elyakova, L. A., Shevchenko, N. M., & Avaeva, S. M. (1981). A comparative study of carbohydrase activities in marine invertebrates. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Comparative Biochemistry, 69(4), 905-908.
- Fernando, M. 2012. Provisional Checklist of Marine Aquatic Shelled Molluscs Of Sri Lanka. Gastropods. The National Red List 2012 of Sri Lanka, 6, 384.
- Fiege, D., Neumann, V., & Li, J. (1994). Observations on coral reefs of Hainan island, South China sea. Marine pollution bulletin, 29(1), 84-89.
- Fields, J. (2013). Effects of Ocean Acidification on the Behavior of Two Marine Invertebrates: A Study of Predator-prey Responses of the Molluscs Conus Marmoreus and Strombus Luhuanus at Elevated-CO2 Conditions.
- FLOOD, N. (1978). HABITUATION OF LIGHT-EVOKED RESPONSES IN A MARINE GASTROPOD, STROMBUS-LUHUANUS. In PACIFIC SCIENCE Vol. 32, No. 1, pp. 96-96
- Frank, P. W. (1969). Growth rates and longevity of some gastropod mollusks on the coral reef at Heron Island. Oecologia, 2(2), 232-250.
- GILLARY, H. L. (1974). Light-evoked electrical potentials from the eye and optic nerve of Strombus: response waveform and spectral sensitivity. Journal of Experimental Biology, 60(2), 383-396.
- Gillary, H. L. (1977). Electrical potentials from the eye and optic nerve of Strombus: effects of electrical stimulation of the optic nerve. Journal of Experimental Biology, 66(1), 159-171.
- Gillary, H. L., & Gillary, E. W. (1979). Ultrastructural features of the retina and optic nerve of Strombus luhuanus, a marine gastropod. Journal of Morphology, 159(1), 89-115.
- GILLARY, H. L. (1983). Electrical potentials from the regenerating eye of Strombus. Journal of experimental biology, 107(1), 293-310.
- Goiran, C. (1990). Etude d'un mollusque Strombidae du lagon sudouest de la Nouvelle-Calédonie: Strombus luhuanus. Noumea: ORSTOM. Mémoire de DEA: Sciences de la Mer: Biol. mar, 31.
- Goniastrea, A., & Pocillopora, M. (2008). CORAL COMMUNITIES OF BARRIER REEFS OF VIETNAM 145. Russian Journal of Marine Biology, 34(1-4), 144.
- Gonor, J. J. (1966). Escape responses of North Borneo strombid gastropods elicited by the predatory prosobranchs Aulica vespertilio and Conus marmoreus. Veliger, 8, 226-230.
- Higuchi, M., Koyano, T., Ito, A., & Wada, S. (2004). Predator avoidance of the conch snail Strombus luhuanus. Suisanzoshoku (Japan).
- Horiguchi, T., Shiraishi, H., Shimizu, M., Yamazaki, S., & Morita, M. (1995). Imposex in Japanese gastropods (Neogastropoda and Mesogastropoda): effects of tributyltin and triphenyltin from antifouling paints. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 31(4), 402-405.
- Horiguchi, T., Cho, H. S., Shiraishi, H., Kojima, M., Kaya, M., Morita, M., & Shimizu, M. (2001). Contamination by organotin (tributyltin and triphenyltin) compounds from antifouling paints and endocrine disruption in marine gastropods. RIKEN REVIEW, 9-11.
- Huelsken, T., Tapken, D., Dahlmann, T., Wägele, H., Riginos, C., & Hollmann, M. (2012). Systematics and phylogenetic species delimitation within Polinices sl (Caenogastropoda: Naticidae) based on molecular data and shell morphology. Organisms Diversity & Evolution, 12(4), 349-375.
- Ishii, T., Miyazaki, T., Nakahara, M., Nakamura, R., & Watabe, T. (1998). STRAWBERRY CONCH STROMBUS LUHUANUS. C JOJ f, 5, 493.
- Johannes, R. E., & MacFarlane, J. W. (1991). Traditional fishing in the Torres Strait islands. CSIRO Division of Fisheries, Marine Laboratories.
- Katsuno, S., & Sasaki, T. (2008). Comparative histology of radula-supporting structures in Gastropoda. Malacologia, 50(1), 13-56.
- Kinch, J. (2003). Marine mollusc use among the women of Brooker Island, Louisiage Archipelago, Papua New Guinea. SPC Women in Fisheries Information Bulletin, 13, 5-14.
- Kinch, J. L’exploitation des mollusques marins par les femmes de l’île Brooker, de l’archipel de la Louisiade, en Papouasie-Nouvelle-Guinée.
- Kirch, P. V. (1985). A radiocarbon chronology for the Mussau Islands. Lapita and its transformations in Near Oceania: archaeological investigations in the Mussau Islands, Papua New Guinea, 88, 196-236.
- Knudsen, J. (1992). PRELIMINARY LIST OF COMMON MARINE PROSOBRANCH GASTROPODS (MOLLUSCA) FROM HOI HA WAN. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Marine Biological Workshop: The Marine Flora and Fauna of Hong Kong and Southern China: Introduction, taxonomy and ecology (Vol. 2, p. 919). Hong Kong Univ. Press.
- Koyano, T., & Wada, S. (2004). Effect of fishery on density of the strawbewrry conch, Strombus luhuanus in Uranouchi Inlet, Tosa Bay, Japan. Suisanzoshoku (Japan).
- Kuwamura, T., Fukao, R., Nishida, M., Wada, K., & Yanagisawa, Y. (1983). Reproductive biology of the gastropod Strombus luhuanus (Strombidae). Publications of the Seto Marine Biological Laboratory, 28(5-6), 433-443.
- Laade, W. (1969). Namen und Gebrauch einiger Seemuscheln und-schnecken auf den Murray Islands, Torres Straits. Linden-Museum.
- Lai, J. R. (2009). Molecular phylogeny of Thatcheria mirabilis and the Superfamily of Conoidea.
- Latama, G., & Nessa, M. N. (1994). GASTROPOD DISTRIBUTION AND ABUNDANCE AROUND KODINGARENG KEKE ISLAND, SOUTH SULAWESI, INDONESIA. In Proceedings of the Fourth Workshop of the Tropical Marine Mollusc Programme (TMMP) at Prince of Songkla University, Thailand and Phuket Marine Biological Center, Thailand, 1993 (No. 13, p. 163).
- Latypov, Y. Y., & Selin, N. I. (2008). Coral communities of barrier reefs of Vietnam. Russian Journal of Marine Biology, 34(3), 143-150.
- Lee, S. C., & Chao, S. M. (2004). Shallow-water marine shells from Kenting National Park, Taiwan. Collection and Research, 17, 33-57.
- Lee, S. C., & Chao, S. M. Shallow-water Marine Shells from the Mouth of Baoli River, Southern Taiwan.
- Lee, J., & Park, J. K. (2013). Morphological Description of a Newly Recorded Strombus luhuanus (Strombidae: Gastropoda) from Korea. Journal of Animal Systematics, Evolution and Diversity, 2
- Lischke, C. E. (1869). Japanische Meeres-Conchylien: ein Beitrag zur Kenntniss der Mollusken Japan's, mit besonderer Rèucksicht auf die geographische Verbreitung derselben. Theodor Fischer.
- Li, Changlin, Liu, Ertian, Li, Tingyou, Wang, Aimin, Liu, Chunsheng, and Gu, Zhifeng, 2019, "Suitability of three seaweeds as feed in culturing strawberry conch Strombus luhuanus" Aquaculture pp 734-761
- Munro, J. L. (1999). Utilization of coastal molluscan resources in the tropical Insular Pacific and its impacts on biodiversity. Marine/Coastal biodiversity in the tropical island Pacific region, 2, 127-144.
- O'Connor, S., Spriggs, M., & Veth, P. (2002). Direct dating of shell beads from Lene Hara Cave, East Timor. Australian Archaeology, (55), 18.
- O'Connor, S., Barham, A., Spriggs, M., Veth, P., Aplin, K., & St Pierre, E. (2010). Cave archaeology and sampling issues in the tropics: A case study from Lene Hara Cave, a 42,000 year old occupation site in East Timor, Island Southeast Asia. Australian Archaeology, (71), 29.
- Ozaki, K., Terakita, A., Hara, R., & Hara, T. (1986). Rhodopsin and retinochrome in the retina of a marine gastropod, Conomurex luhuanus. Vision research, 26(5), 691-705.
- Parr, J. F., & Carter, M. (2003). Phytolith and starch analysis of sediment samples from two archaeological sites on Dauar Island, Torres Strait, northeastern Australia. Vegetation History and Archaeobotany, 12(2), 131-141.
- Parsons-Hubbard, K. M., Callender, W. R., Powell, E. N., Brett, C. E., Walker, S. E., Raymond, A. L., & Staff, G. M. (1999). Rates of burial and disturbance of experimentally-deployed molluscs; implications for preservation potential. Palaios, 14(4), 337-351.
- Pernetta, J. C., & Hill, L. (1981). A review of marine resource use in coastal Papua. Journal de la Société des Océanistes, 37(72), 175-191.
- Petchey, F., Ulm, S., David, B., McNiven, I. J., Asmussen, B., Tomkins, H., ... & Stanisic, J. (2012). 14C marine reservoir variability in herbivores and deposit-feeding gastropods from an open coastline, Papua New Guinea. Radiocarbon, 54, 967-978.
- Petri, H. (1936). Die Geldformen der Südsee.(Schluß). Anthropos, 509-554.
- Petuch, E. J. (1982). Paraprovincialism: Remnants of paleoprovincial boundaries in Recent marine molluscan provinces. Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington, 95(4), 774-780.
- Poiner, I. R., & Catterall, C. P. (1988). The effects of traditional gathering on populations of the marine gastropod Strombus luhuanus Linne 1758, in southern Papua New Guinea. Oecologia, 76(2), 191-199.
- Powell, E. N., & Cummins, H. (1985). Are molluscan maximum life spans determined by long-term cycles in benthic communities?. Oecologia, 67(2), 177-182.
- QUANDT, F. N., & GILLARY, H. L. (1979). Classes of light-evoked response in the retina of Strombus. Journal of Experimental Biology, 80(1), 287-297.
- Reed, S. E. (1995). Sexual trimorphism in Strombus luhuanus (Mollusca: Gastropoda) at Shirahama, Japan. Journal of Shellfish Research, 14(1), 159-160.
- Richardson-White, S., & Walker, S. E. (2011). Diversity, taphonomy and behavior of encrusting foraminifera on experimental shells deployed along a shelf-to-slope bathymetric gradient, Lee Stocking Island, Bahamas. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 312(3), 305-324.
- Ritchie, M. (1986). A Study of the Movement Behaviour of the Benthic Marine Gastropod Strombus Luhuanus (Linne) on the Subtidal Reef Flat of Heron Island, Great Barrier Reef (Doctoral dissertation, Griffith University).
- Rivierre, J. C. (1973). La nomenclature des coquillages dans la langue de Touho. Journal de la Société des océanistes, 29(39), 139-150.
- Sanchez-Escalona, K. (2011). Geometric morphometrics as a tool in discriminating population of Strombus luhuanus. In 11th National Symposium in Marine Science.
- Sanchez-Escalona, K.P., Aliño, P.A., Juinio-Meñez, Ma.A. 2017. Evidence of shape Sexual dimorphism in Strombus luhuanus linnaeus 1758 (Gastropoda: Strombidae); Journal of Conchology, 42 (6), pp. 395-400.
- Serb, J. M., & Eernisse, D. J. (2008). Charting evolution’s trajectory: using molluscan eye diversity to understand parallel and convergent evolution. Evolution: Education and Outreach, 1(4), 439-447.
- Shiba, K., Shibata, D., & Inaba, K. (2014). Autonomous changes in the swimming direction of sperm in the gastropod Strombus luhuanus. The Journal of experimental biology, 217(6), 986-996.
- Shirayama, Y., & Thornton, H. (2005). Effect of increased atmospheric CO2 on shallow water marine benthos. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans (1978–2012), 110(C9).
- Smith, B. D. (2003). Prosobranch gastropods of Guam. Micronesica, 35(36), 244-270.
- Stephenson, W., Endean, R., & Bennett, I. (1958). An ecological survey of the marine fauna of Low Isles, Queensland. Marine and Freshwater Research, 9(2), 261-318.
- Swadling, P. (1976). Changes induced by human exploitation in prehistoric shellfish populations. Mankind, 10(3), 156-162.
- Swadling, P., & Chowning, A. (1981). Shellfish gathering at Nukalau Island, West New Britain Province, Papua New Guinea. Journal de la Société des Océanistes, 37(72), 159-167.
- Szabo, K., & Ramirez, H. (2009). Worked shell from Leta Leta Cave, Palawan, Philippines. Archaeology in Oceania, 44(3), 150-159.
- Taylor, J. D., & Shin, P. K. (1990). Trawl surveys of sublittoral gastropods in Tolo Channel and Mirs Bay; a record of change from 1976–1986 (pp. 1203-1220).
- Thomas, F. R. (2001). Mollusk habitats and fisheries in Kiribati: an assessment from the Gilbert Islands. Pacific Science, 55(1), 77-97.
- Thomas, F. R. (2002). An evaluation of central-place foraging among mollusk gatherers in Western Kiribati, Micronesia: Linking behavioral ecology with ethnoarchaeology. World Archaeology, 34(1), 182-208.
- Thomas, F. R. (2007). The behavioral ecology of shellfish gathering in western Kiribati, Micronesia 1: Prey choice. Human Ecology, 35(2), 179-194.
- Thomas, F. (2007). The behavioral ecology of shellfish gathering in Western Kiribati, Micronesia. 2: Patch choice, patch sampling, and risk. Human Ecology, 35(5), 515-526.
- Tsi, C. Y., & Ma, S. T. (1982, April). A preliminary checklist of the marine Gastropoda and Bivalvia (Mollusca) of Hong Kong and southern China. In Proceedings of the First International Workshop on the Malacofauna of Hong Kong and Southern China, Hong Kong University Press, Hong Kong (pp. 431-458).
- Vermeij, G. J. (1979). Shell architecture and causes of death of Micronesian reef snails. Evolution, 686-696.
- Veron, J. E. N. (2002). Reef corals of the Raja Ampat Islands, Papua Province, Indonesia. A Marine Rapid Assessment of the Raja Ampat Islands, Papua Province, Indonesia, 26.
- Volta, 1787
- Wada, K., Fukao, R., Kuwamura, T., Nishida, M., & Yanagisawa, Y. (1983). Distribution and growth of the gastropod Strombus luhuanus at Shirahama, Japan. Publications of the Seto Marine Biological Laboratory, 28(5-6), 417-432.
- Walker, S. E., Parsons-Hubbard, K., Powell, E., & Brett, C. E. (2002). Predation on experimentally deployed molluscan shells from shelf to slope depths in a tropical carbonate environment. Palaios, 17(2), 147-170.
- Watters, G. T., & Valentine, B. P. (1994). Strombus luhuanus L., 1758, and Strombus urceus urceus L., 1758, in the Indian Ocean. Hawaiian Shell News, 42(4), 8-9.
- Way, K., & Purchon, R. D. (1981). THE MARINE SHELLED MOLLUSCA OF WEST MALAYSIA AND SINGAPORE PART 2. POLYPLACOPHORA AND GASTROPODA. Journal of Molluscan Studies, 47(3), 313-321.
- Weis, A., Dunning, M., & Gaffney, P. (2004). Ecological assessment of Queensland’s Marine Specimen Shell Collection Fishery.
- Wells, F. E. (2005). Molluscs of the Phuket region, Thailand. Rapid Assessment Survey of Tsunami-affected Reefs of Thailand, 57.
- Wiedemeyer, W. L. (1998). Contributions to the larval biology of the red‐lipped conch, Strombus luhuanus L. 1758, with respect to seed production for mariculture. Aquaculture research, 29(1), 1-17.
- Yamaguchi, M. (1994). Molluscan resources from coral reefs. 3-reed-lippet stromb Strombus luhuanus. Aquabiology (1994): 107-111.
Film:
Sequences:
- Nucleotide
- Elongation factor 1 alpha gene, partial cds
- 12S ribosomal RNA gene, partial sequence
- voucher C203214 cytochrome oxidase subunit I (COX1) gene, partial cds; mitochondrial
- voucher C203214 cytochrome oxidase subunit I (COX1) gene, partial cds; mitochondrial
- 28S ribosomal RNA and 28S ribosomal RNA genes, partial sequence
- 28S ribosomal RNA gene, partial sequence
- 28S ribosomal RNA gene, partial sequence
- histone H3 gene, partial cds
- histone H3 (his3) gene, partial cds
- cytochrome oxidase subunit I (COI) gene, partial cds; mitochondrial
- 16S ribosomal RNA gene, partial sequence; mitochondrial gene for mitochondrial product
- Protein
|