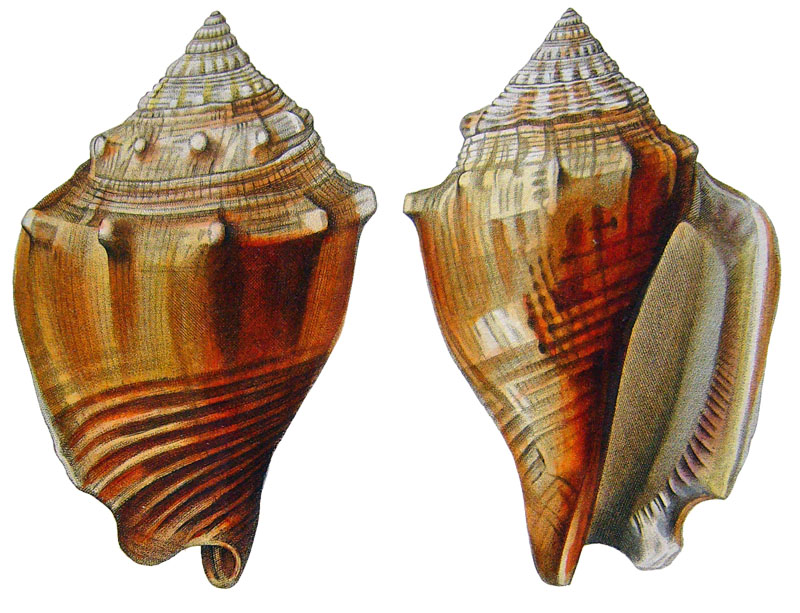
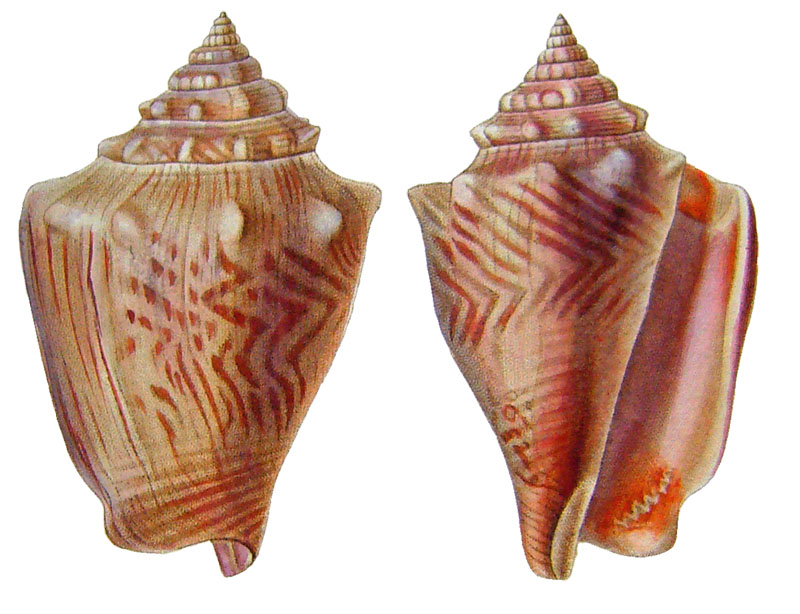
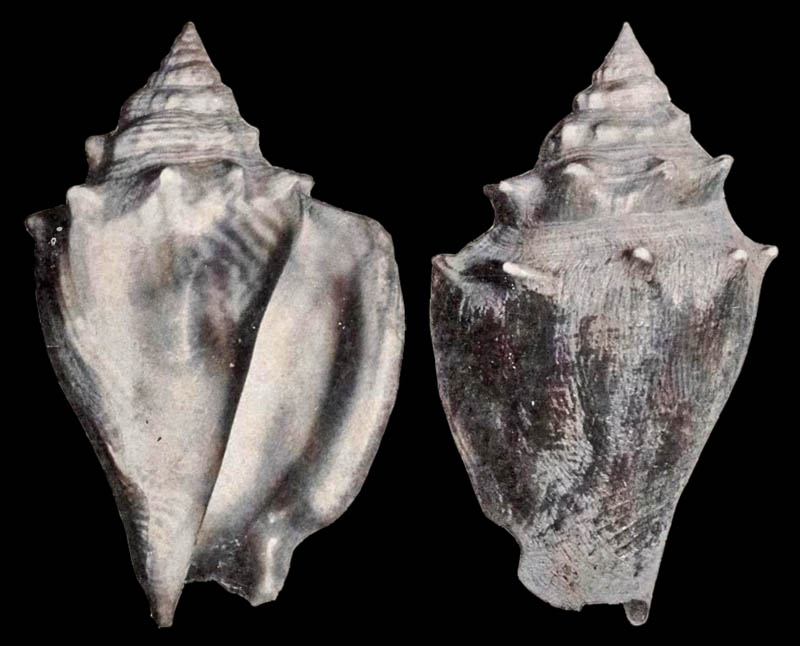
Stromboidea
Original Description of Strombus alatus by Gmelin, 1791, p. 3513:
- "Str. testae labro anteriori prominente rotundato laevi, spira inermi, cauda triloba obtusa."
Gmelin cited:
- Martin. Conch. 3. t. 91. f. 894.
- Schroet. Einl. in Conch. I. p. 454. t. 2. f. 14.
- Habitat --- testa fusca: fascia alba fusco maculata, spira alba fusco radiata et undulata, ventre et columella dilute badiis, cauda incarnata, fauce alba, labro intus fusco caeruleo rubrque nitente, ad marginem incarnato, dorso laevi ad basin tuberculis subacutis coronato."
Locus typicus: Sanibel Island, Lee County, Florida, USA by designation (Goodrich, 1944)
History and Synonymy
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791: 3513
- Syn.: Pyramis crenulata Röding, 1798: 59
- Syn.: Strombus dubius Sowerby. Tryon, 1885: 109 [Non Solander, 1766, nec Swainson, 1823, nec Sowerby 2nd, 1842 nec Kiener, 1843] based on misidentification by Tryon.
- Syn.: Strombus pugilis alatus Goodrich, 1944:
- Syn.: Strombus pyrulatus Lamarck, 1822: 205
- ?Syn.: Strombus pyrulatus var. albicans Sowerby 1st, 1825: 68 [nom. nud.]
- Syn.: Strombus sulcatus Anton, 1838: 85
- Syn.: Strombus undulatus “Chemnitz”. Küster, 1845: 39, pl. 4b figs 3, 4
1822
Strombus pyrulatus Lamarck, 1822: 205
1843
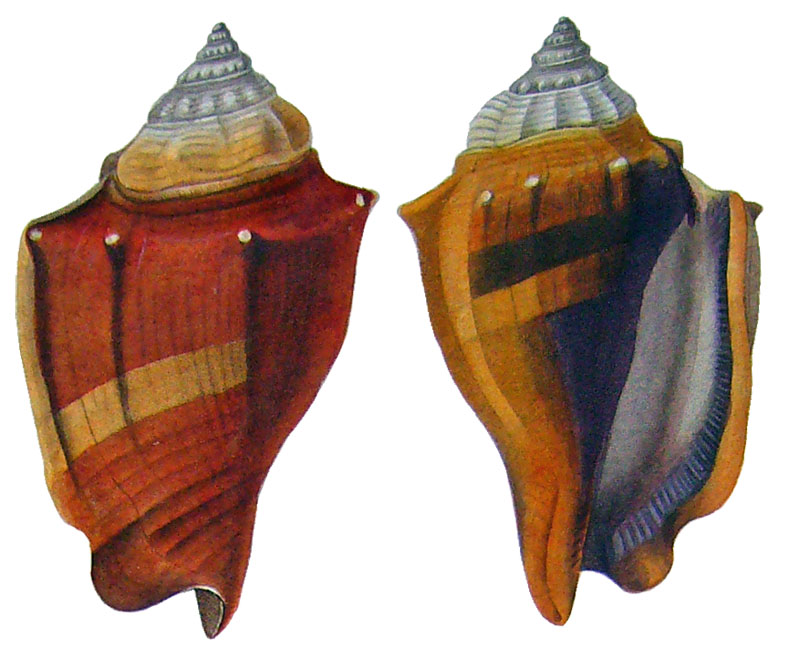
Strombus pyrulatus in Kiener, 1843, pl. ?, fig. 1
Strombus pyrulatus in Kiener, 1843, pl. 34, fig. 2
1844
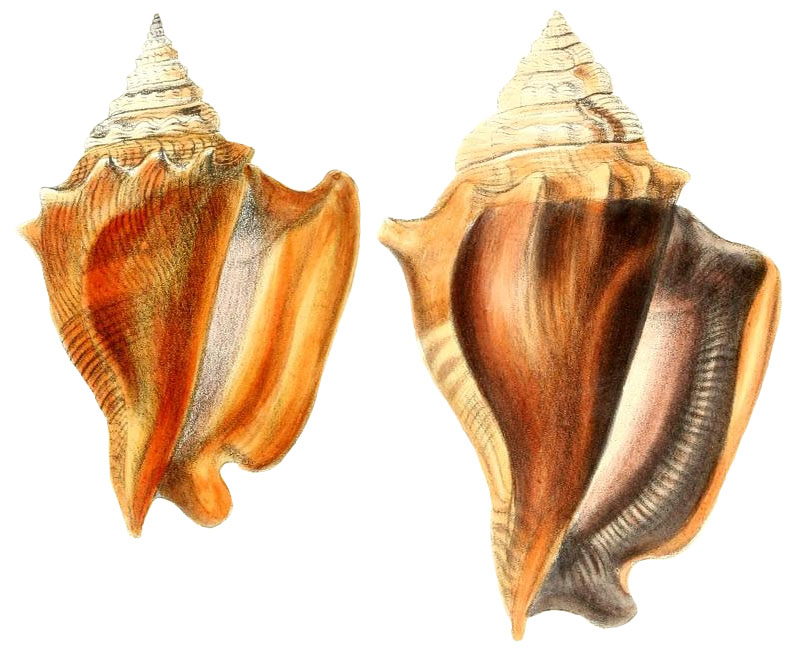
Strombus pyrulatus in Duclos, 1844, pl. 19, fig. 1, 2
Strombus pyrulatus juvenile in Duclos, 1844, pl. 19, fig.7, 8
1851
Strombus alatus in Reeve, 1851, Strombus, pl. 16, fig. 40
1905
Colton, 1905 on sexual dimorphism of Strombus pugilis alatus, p. 140:
- "The average columella angle CDE is for males 37.4° and for females 40.4°. The columella angle of the females is larger than that of the males. This is characteristic, and it is possible to separate the males from the females in a large series at a glance with very few errors."
1941
Strombus pugilis alatus in Clench & Abbott, 1941, p. 7, pl. 5
1944
Goodrich, 1944, p. 2 on Strombus pugilis alatus:
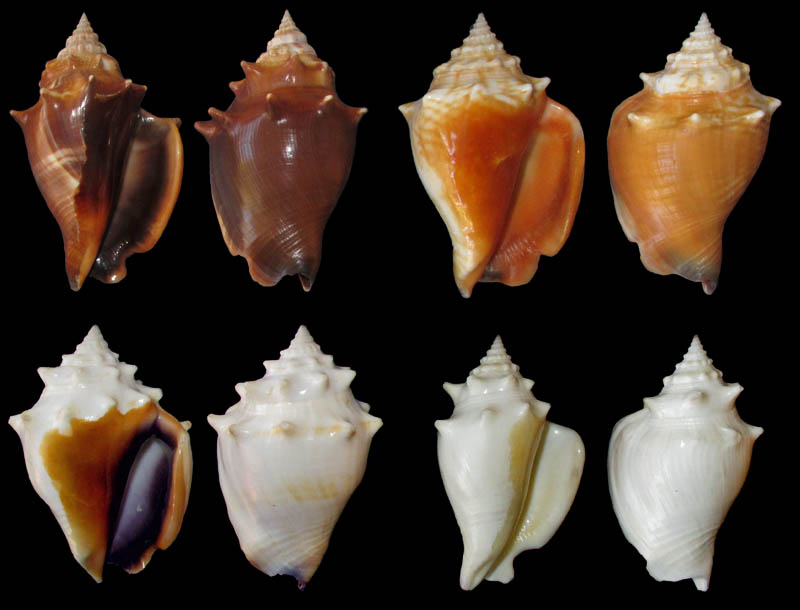
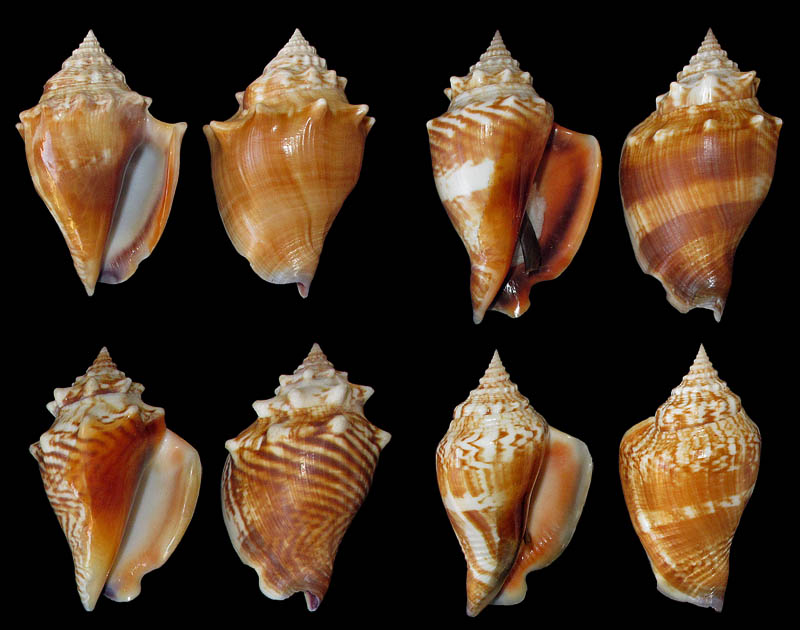
- "In the environment around Sanibel Island, it is both short and long spired, and at every stage between these extremes. Sculpture ranges from feebly nodulous to stoutly spinose. Color is protean, uncorrelated with any other character so far as could be learned. In short, the striking feature of alatus, in contrast to typical pugilis, is the absence of uniformity. Distribution is from North Carolilia to the shores of the Gulf of Mexico in Texas."
1989
Mitton, Berg & Orr, 1989, p. 361:
- "Although Strombus alatus is the most common species of Strombus in northern areas and its planktonic larvae occur in the neritic waters off North Carolina (Thiriot-Quievreux 1983), it disappeared from Bermuda sometime since the Pleistocene, when glaciers forced the GulfStream to the south and into a more east west orientation, bringing it closer to Bermuda (Keffer et al., 1988). Bermuda now lies in the central oceanic gyre of the North Atlantic, more than 1500 km from the Gulf Stream."
2004
Strombus alatus kendrewi Petuch, 2004
2006
Gillette & Shawl, 2006, p. 948:
- "S.alatus is a small (7 - 10 cm) herbivorous conch found along the coasts of North Carolina to Florida and throughout the Gulf of Mexico (Shawl and Spring 2003). S. alatus have a similar life cycle and culture characteristics of queen conch, however, the adults tend to have a more complex breeding behavior. Multiple males have been observed copulating with one female at the same time (Reed 1995, Shawl and Davis 2004). Likewise, a male S. alatus often guards the female with which he mated, and may also encourage “sparring contests” with other males that attempt to mate with her (Shawl and Davis 2004). Males also tend to following females, and have even attempted to copulate with an unguarded female while she was laying an egg mass (Shawl and Davis 2004)."
Specimens from private collections
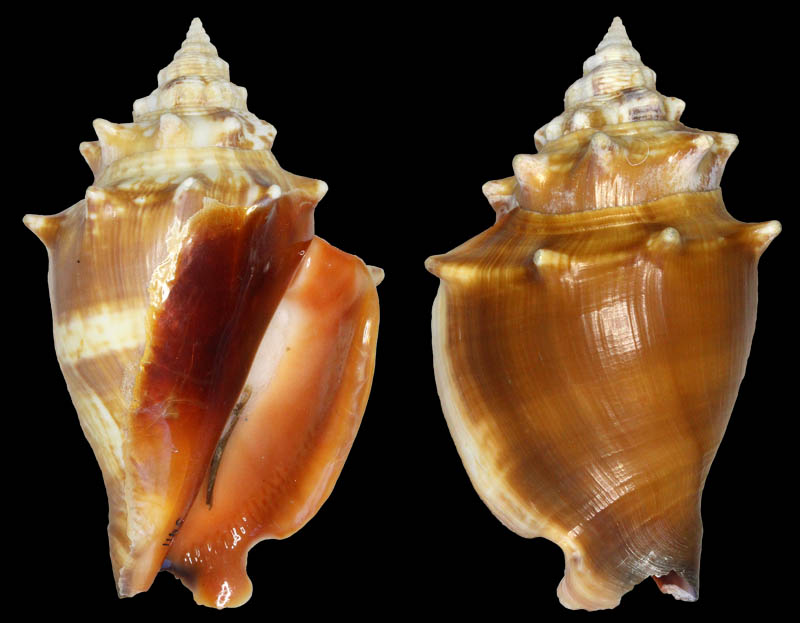
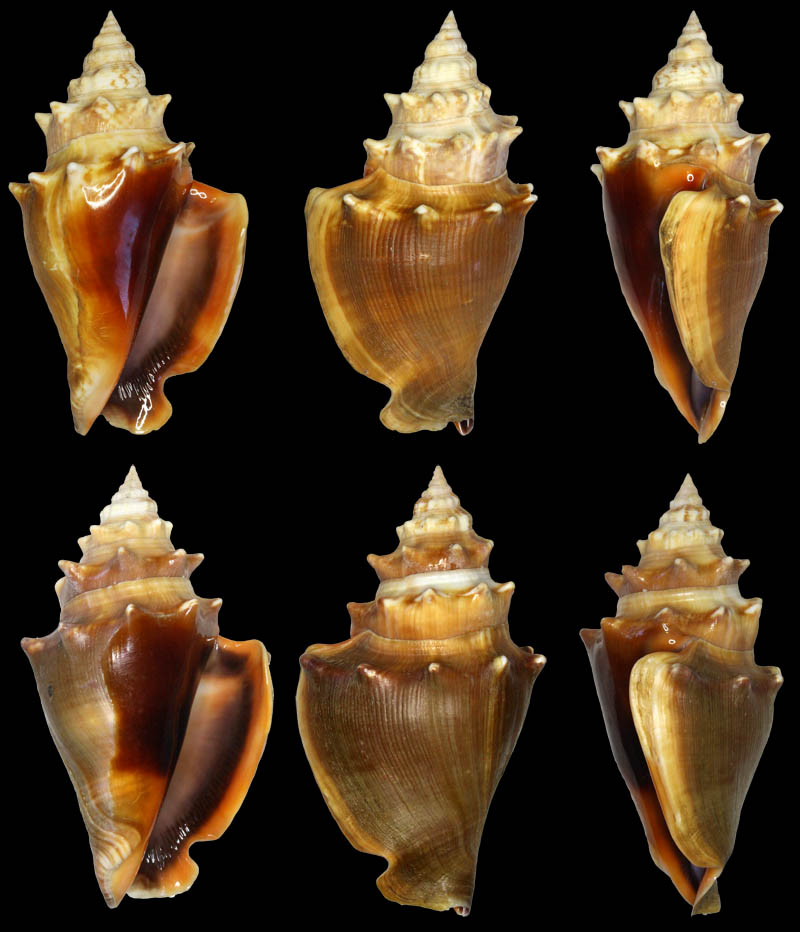
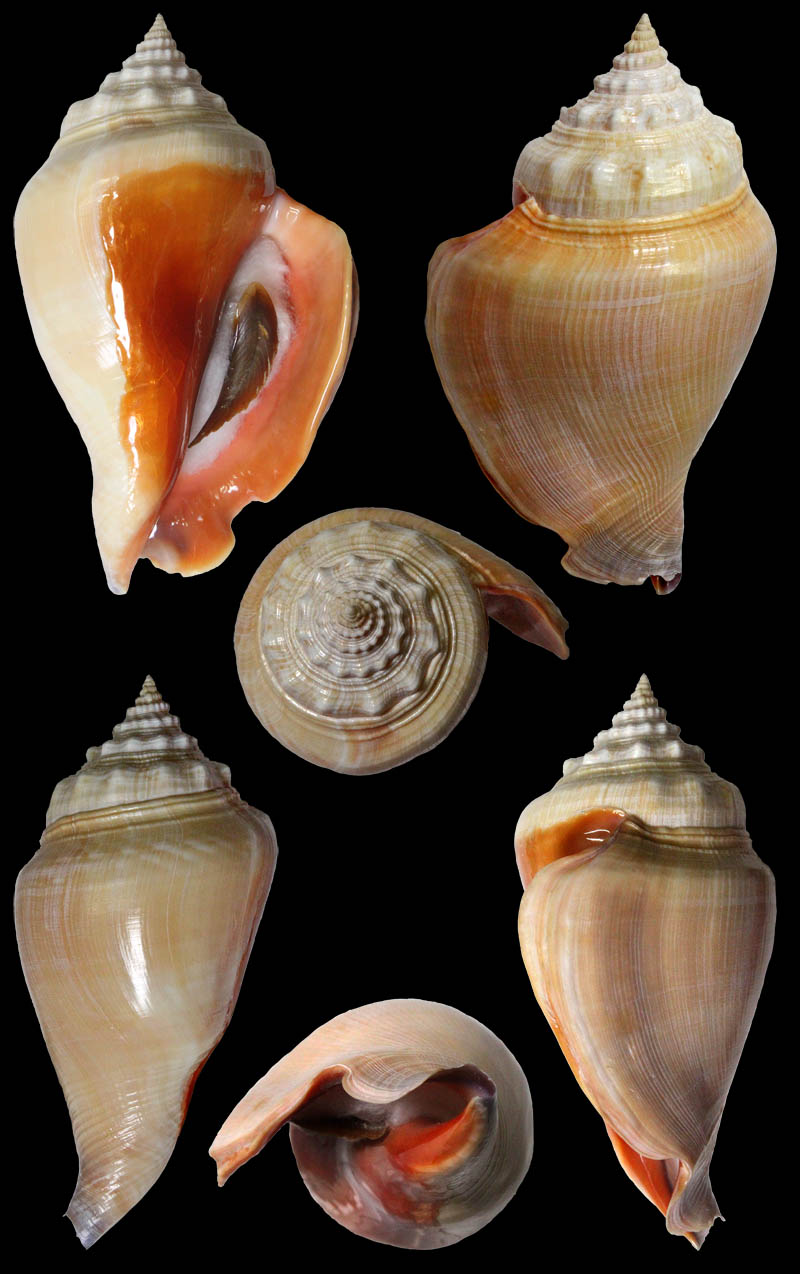
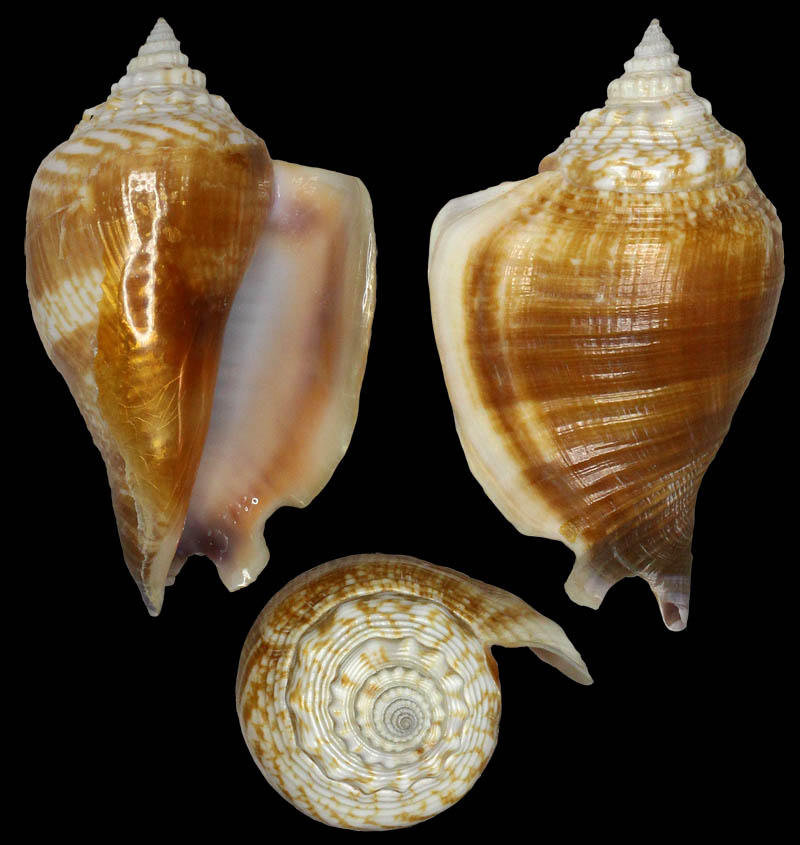
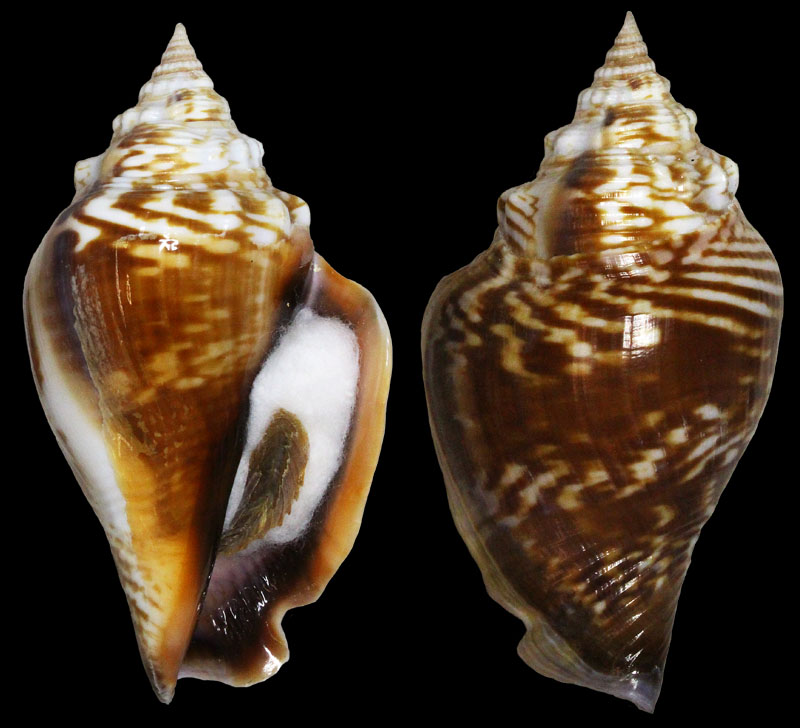
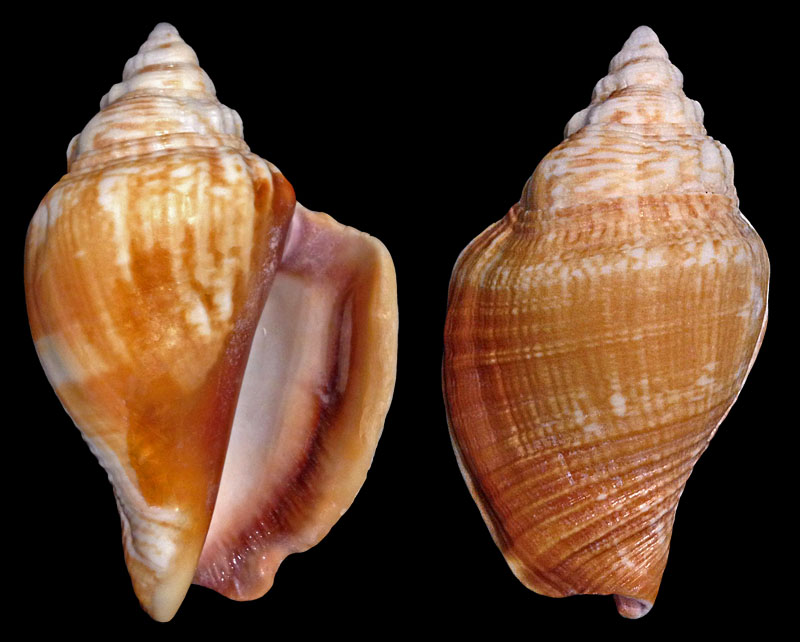
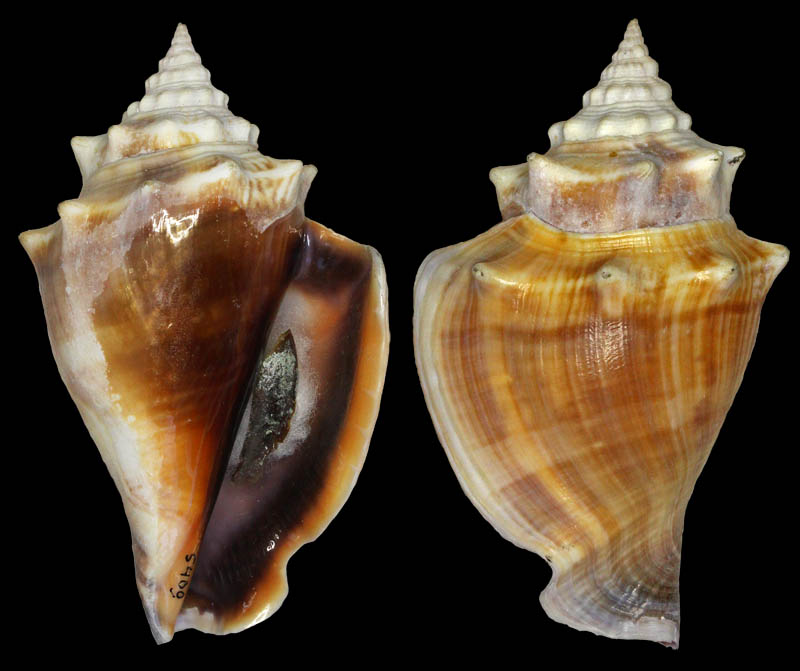
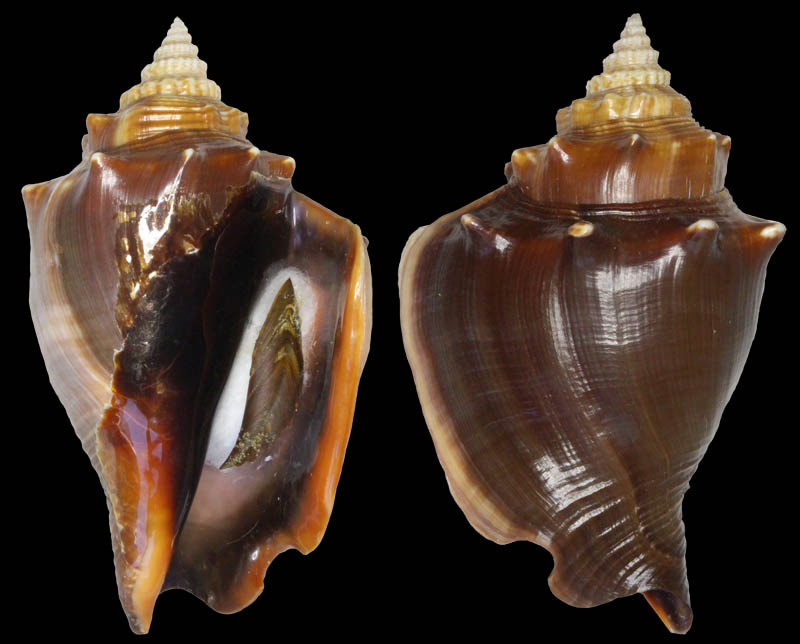
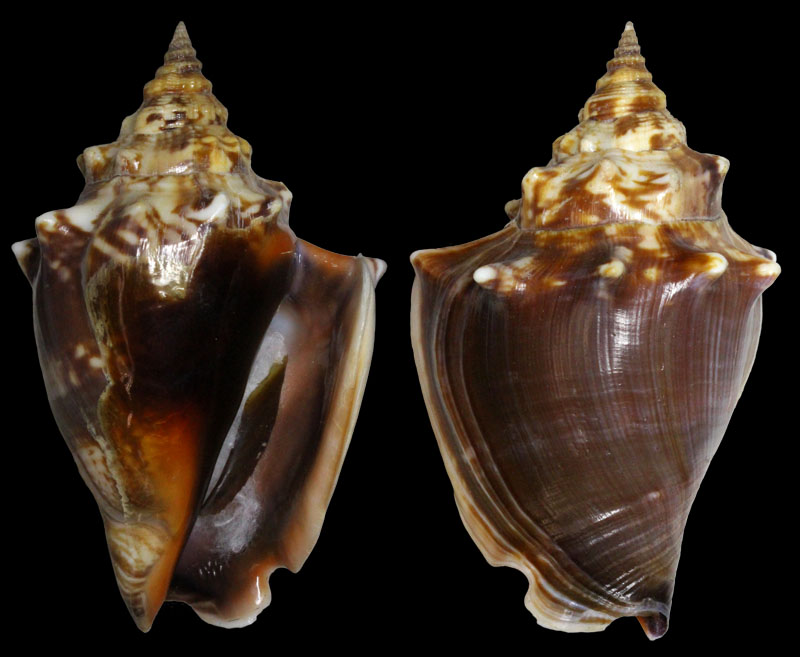
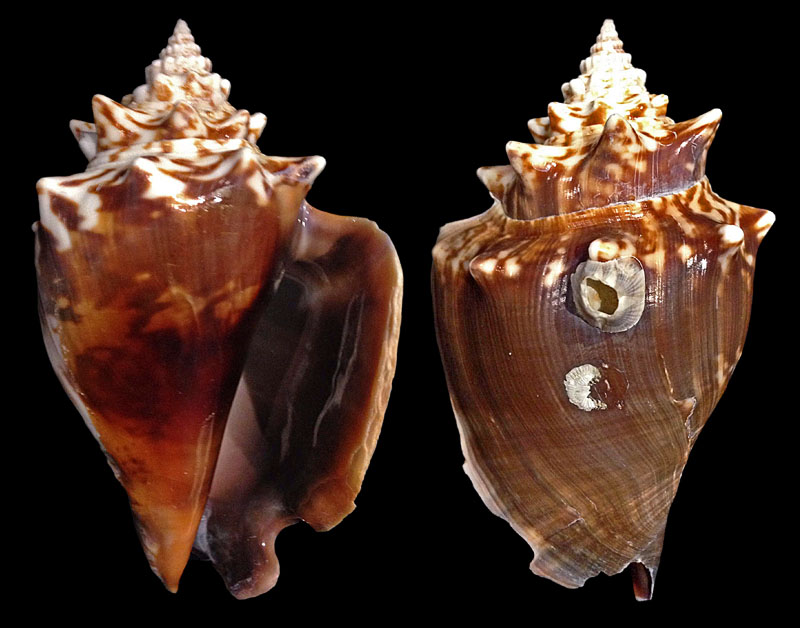
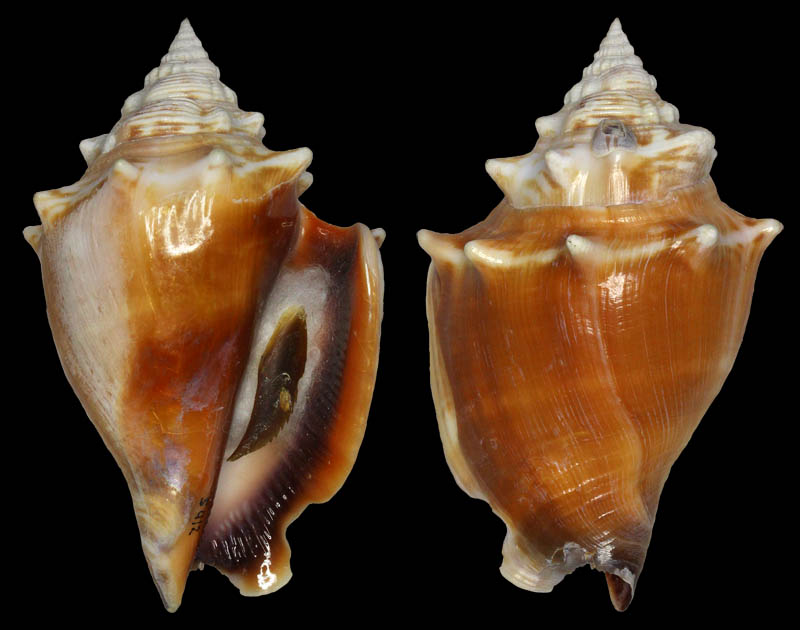
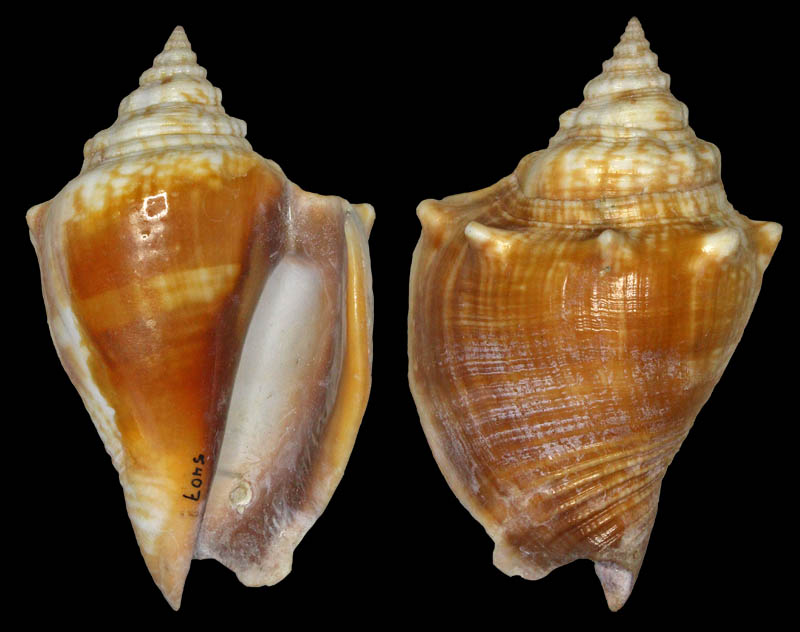
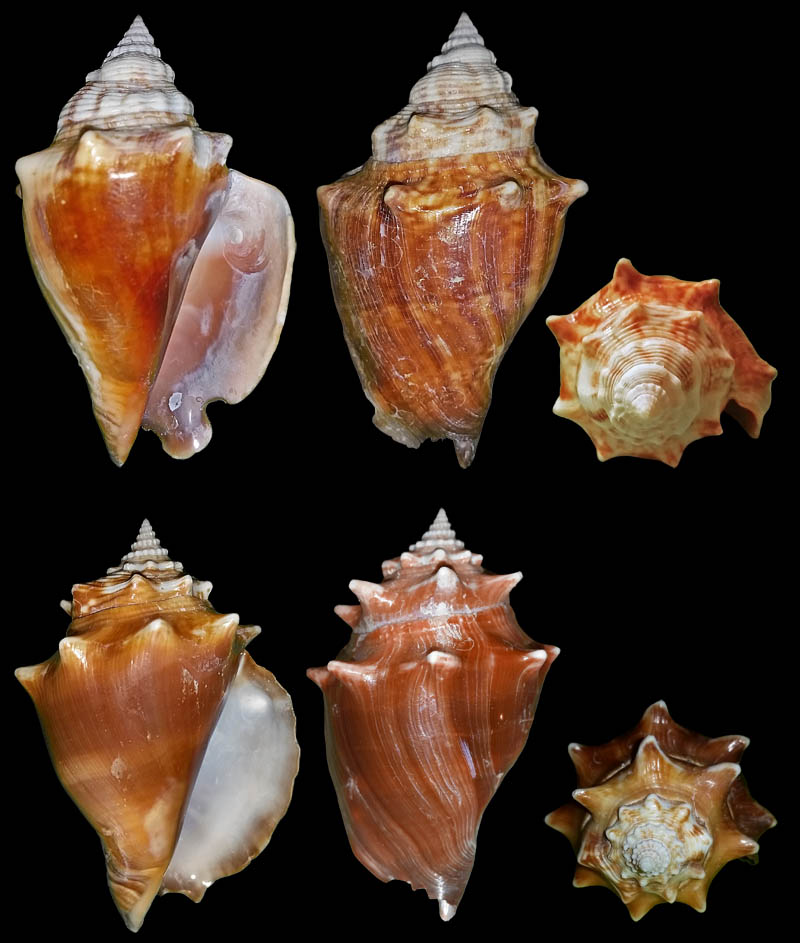
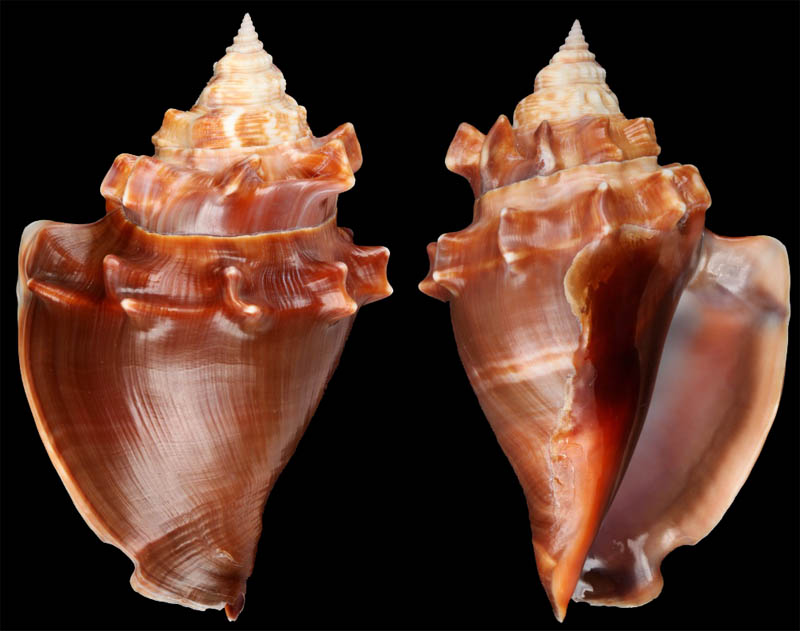
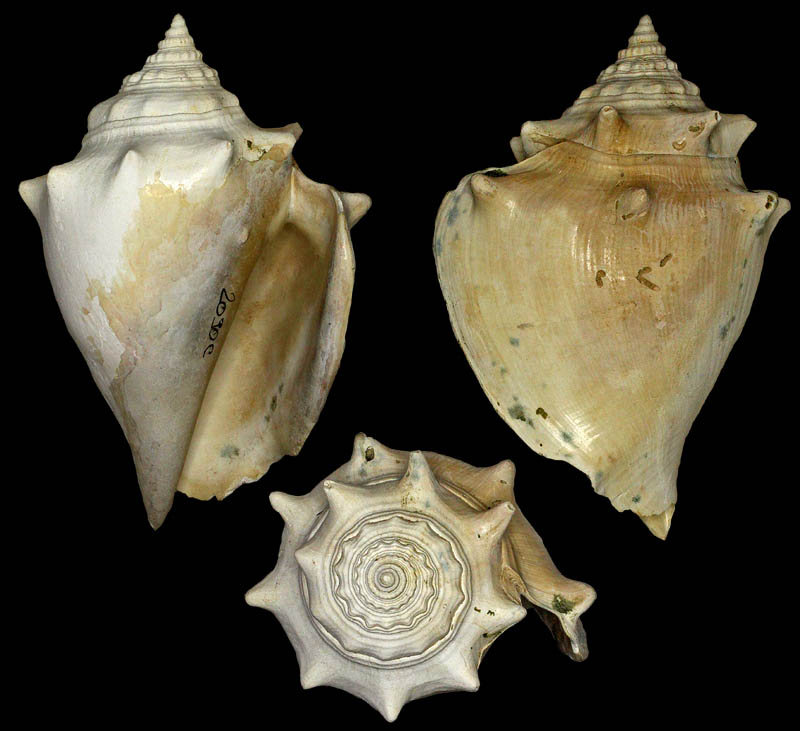
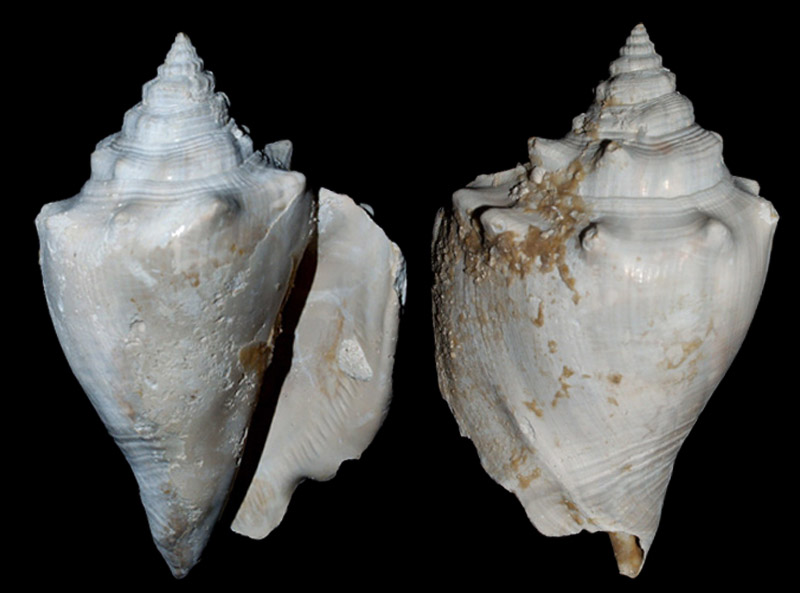
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Fort Worth inlet, Palm Beach County, Florida, USA; at 10'-20' on sand; Coll. Gijs Kronenberg no. 5411
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Riviera Beach, Peanut Island, Palm Beach County, Florida, USA; live collected in eel-grass at 1 m; t: 86 mm, m: 85 mm, b: 84 mm; 5/1985; Coll. Christian Börnke
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Peanut Island, Palm Beach County, Florida, USA; t: 92 mm, b: 95 mm; Coll. Christian Börnke
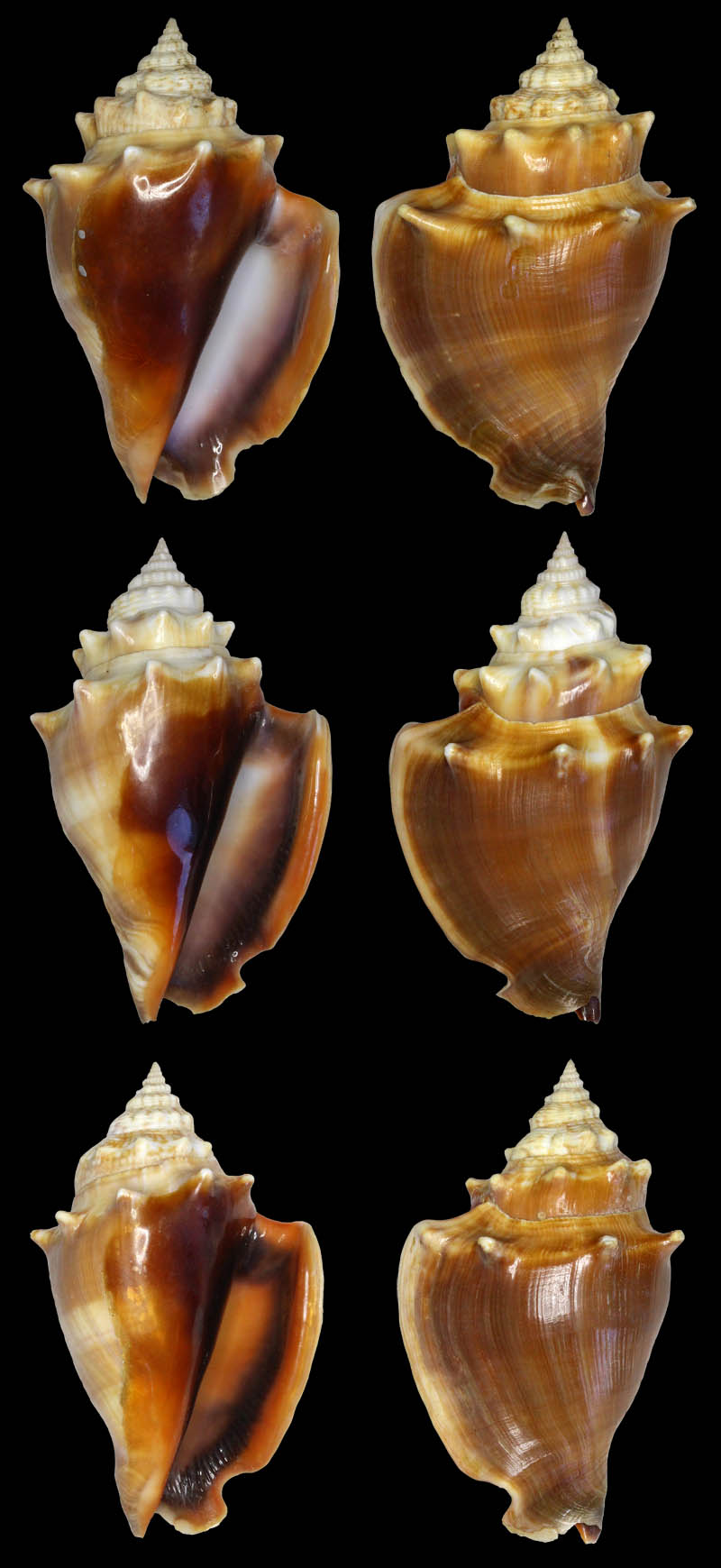
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Punta Rassa, Cape Coral - Fort Myers, Lee County, Florida, USA; low Tide, exposed sand; 93 mm; Coll. Virgilio Liverani
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Palm Beach area, Florida, USA; shallow water; 1985; Coll. Koenraad De Turck
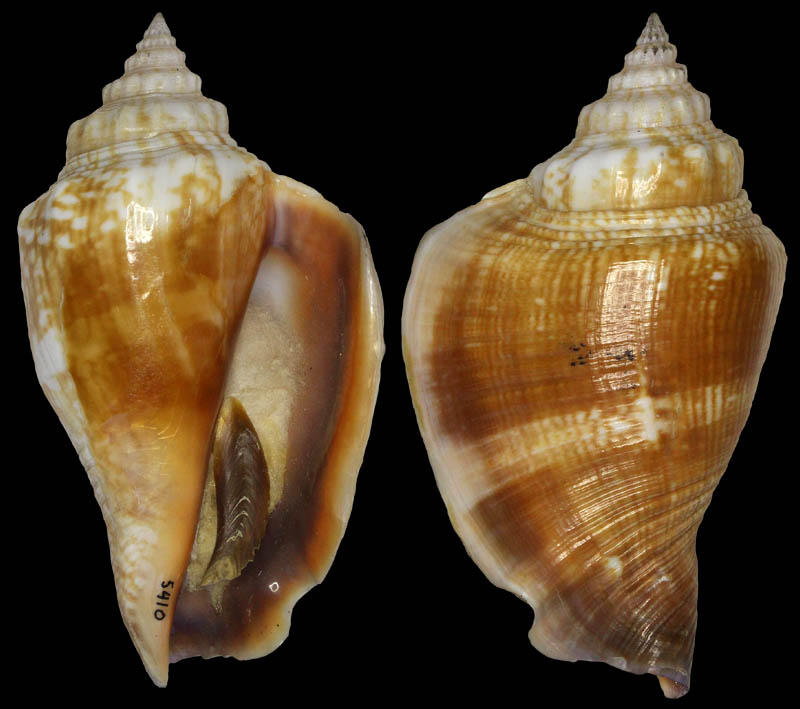
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Florida, USA; Coll. Gijs Kronenberg no. 5410
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Fort Myers, Lee County, Florida, USA; in sandy grass at low tide; 89 mm; Coll. Ulrich Wieneke
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Panama City, Florida, USA; by diver, 120 ft. deep; Coll. Koenraad De Turck
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Florida, USA; 81,7 mm; Coll. Goran Vertriest
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Key Largo, Monroe County, Florida, USA; 1972; Coll. Gijs Kronenberg no. 5413
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Sanibel Island, Lee County, Florida, USA; 1970; coll. Gijs Kronenberg no. 5409
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Sanibel Island, Lee County, Florida, USA; 1970; coll. Gijs Kronenberg no. 4000
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; one mile south of Peanut Island, Lake Worth, Palm Beach, Florida, USA; scuba in 10-15 ft., 6/1989; Coll. Koenraad De Turck
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Florida, USA; 84,6 mm; Coll. Goran Vertriest
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Sanibel Island, Lee County, Florida, USA; by SCUBA at 55' deep; 1988; Coll. Gijs Kronenberg no. 5412
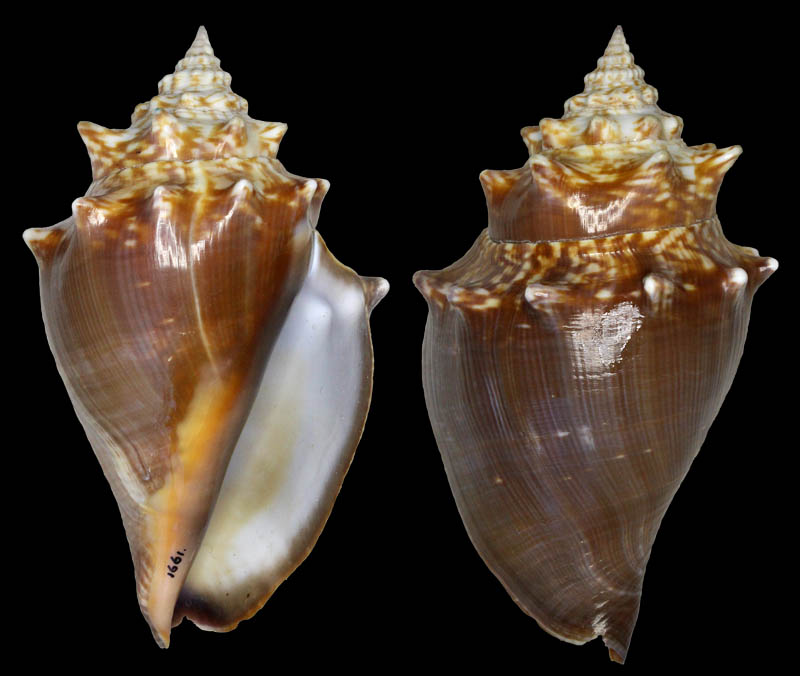
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; subadult; Sanibel Island, Lee County, Florida, USA; Coll. Gijs Kronenberg no. 1661
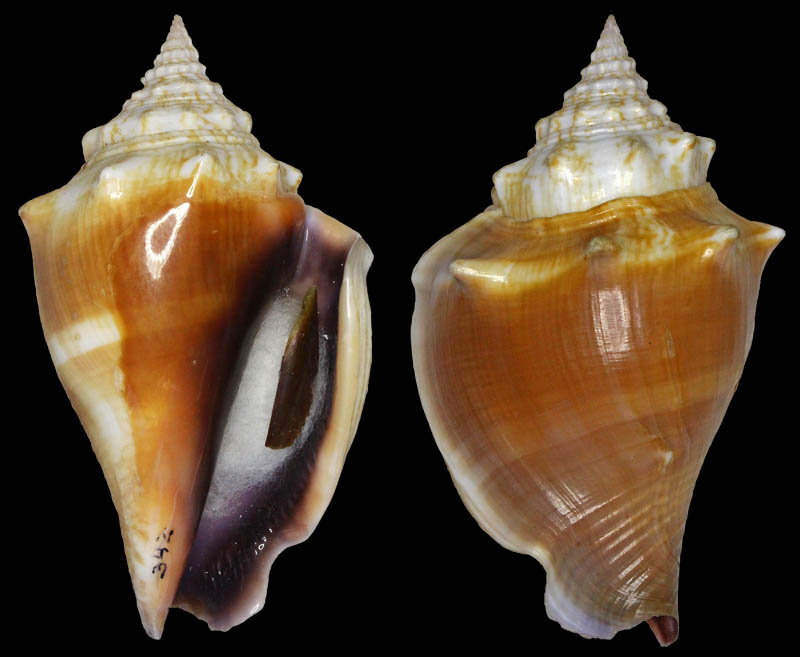
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Centent Key, Monroe County, Florida, USA; Coll. Gijs Kronenberg no. 0342
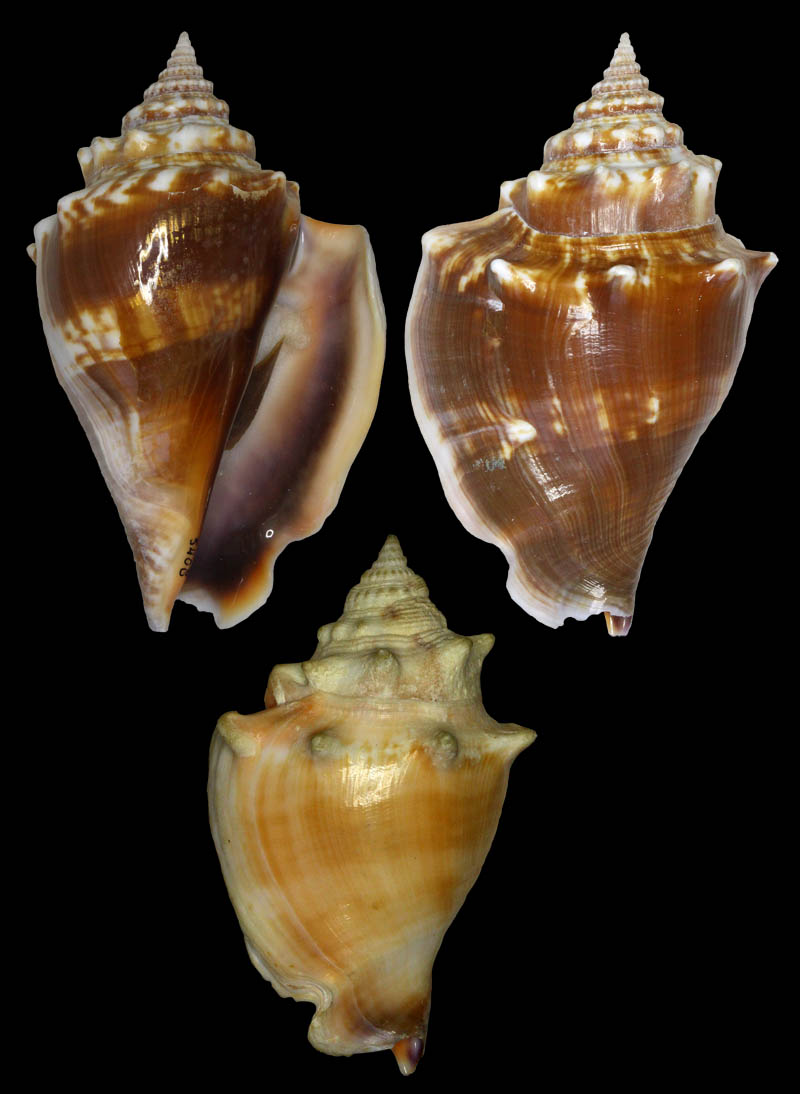
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Keys, Monroe County, Florida, USA; Coll. Gijs Kronenberg no. 5408 (t), 0325(b)
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Estero Island, Lee County, Florida, USA; 11/1973; Coll. Gijs Kronenberg no. 5407
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Pinellas County, Florida, USA; t: 80 mm, b: 74 mm; Coll. David Carroll
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Pinellas County, Florida, USA; t: 85 mm, b: 81 mm; Coll. David Carroll
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; double spined form; collected on exposed sand and grass flats at low tide, Riviera Beach, Peanut Island, Palm Beach County, Florida, USA; July 2003; Coll. Aart Dekkers no. STR0459
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Peanut Island, Palm Beach County, Florida, USA; Length 99.31 mm; Coll. Dennis Sargent
- Comment Dennis Sargent
- Both Strombus alatus and Strombus pugilis can exhibit the anomaly that was described as “sloani Leach, 1814”. This name has no validity and is considered a synonym.
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Big Pine Key, Lower Florida Keys, Florida, USA; 1984; Coll. Koenraad De Turck
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Coll. Paul Kanner
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Coll. Paul Kanner
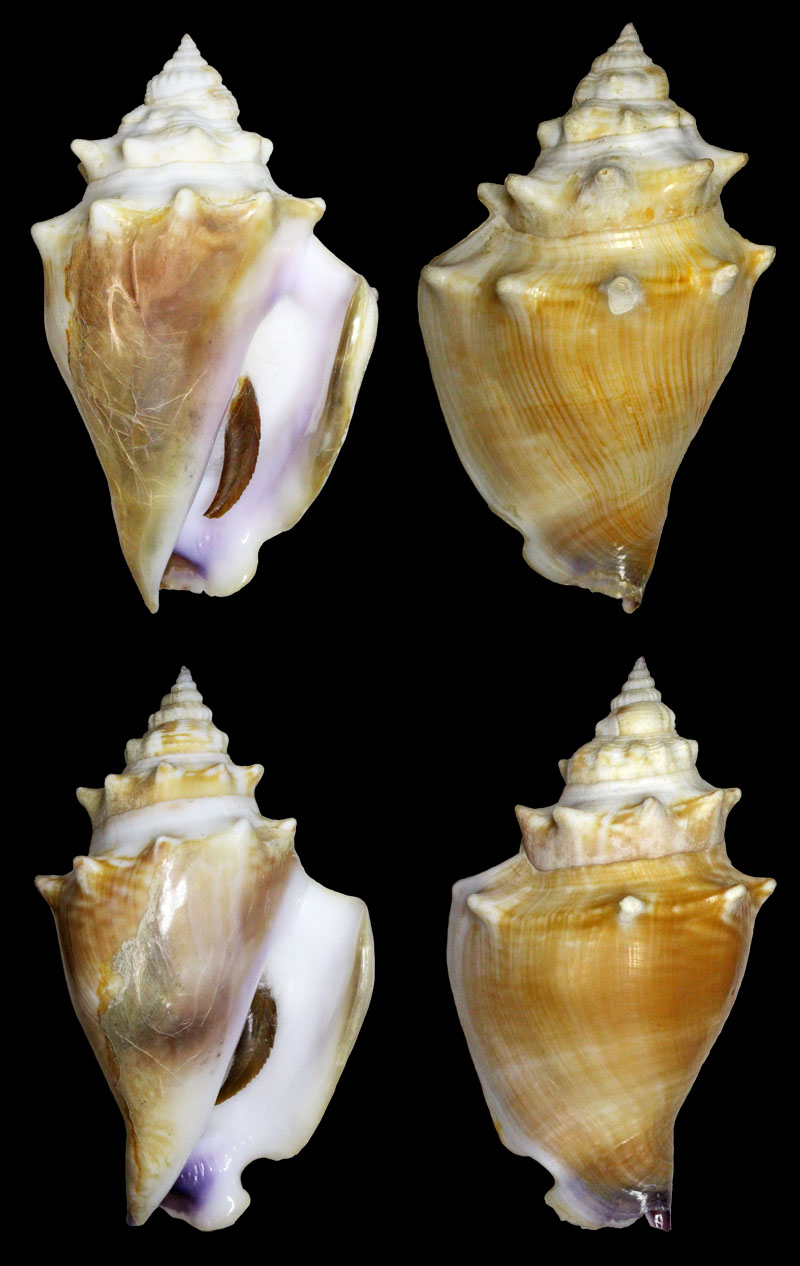
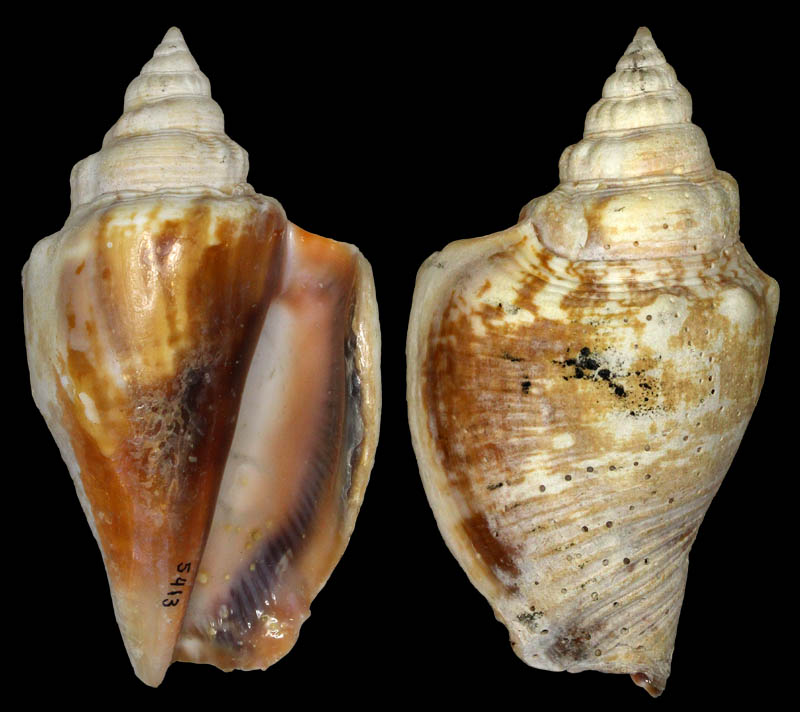
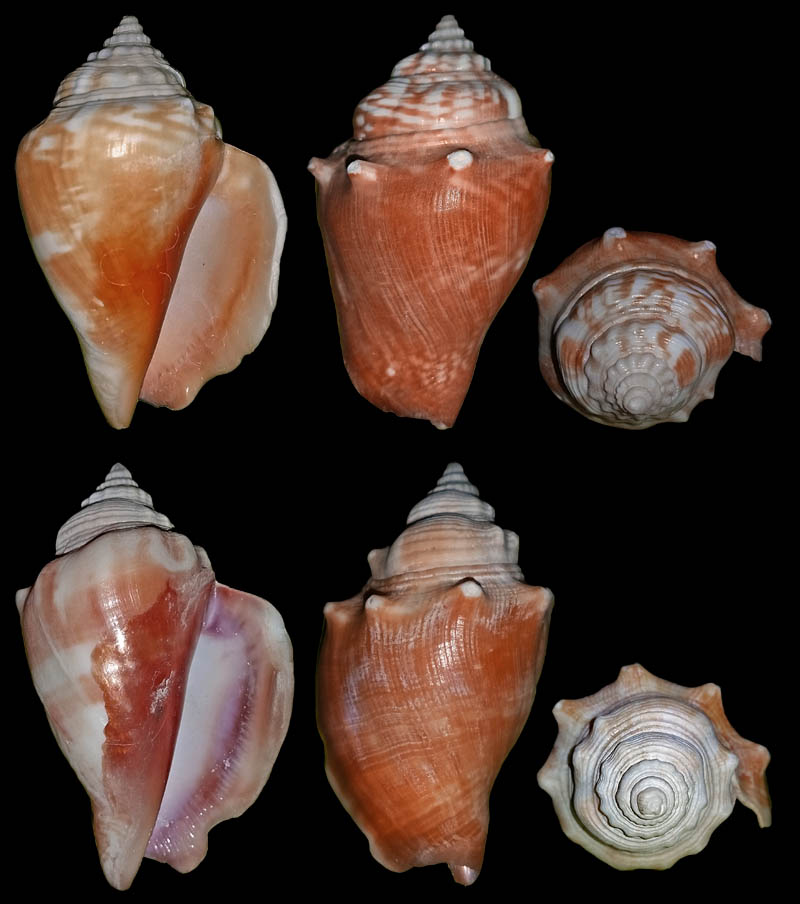
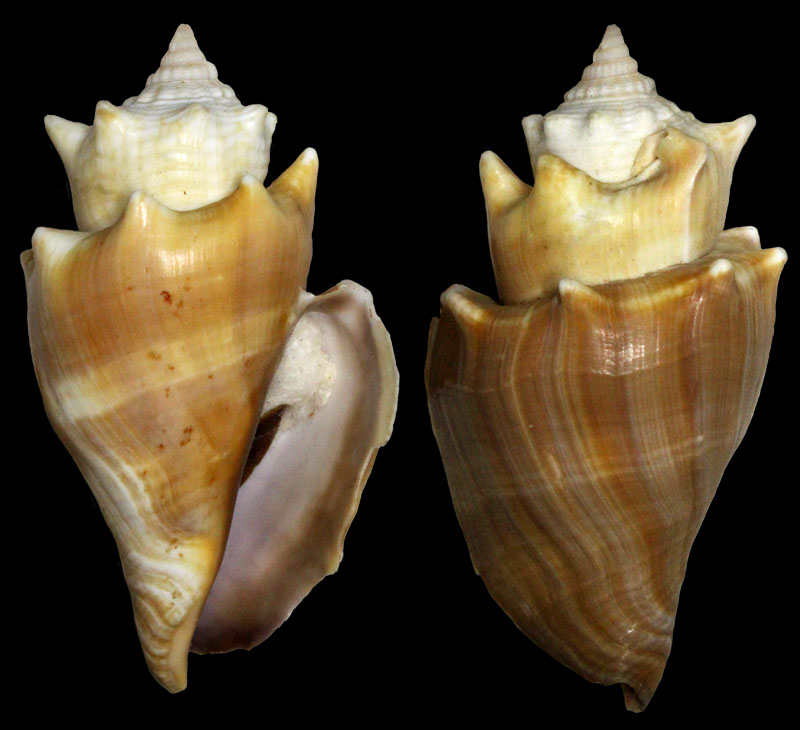
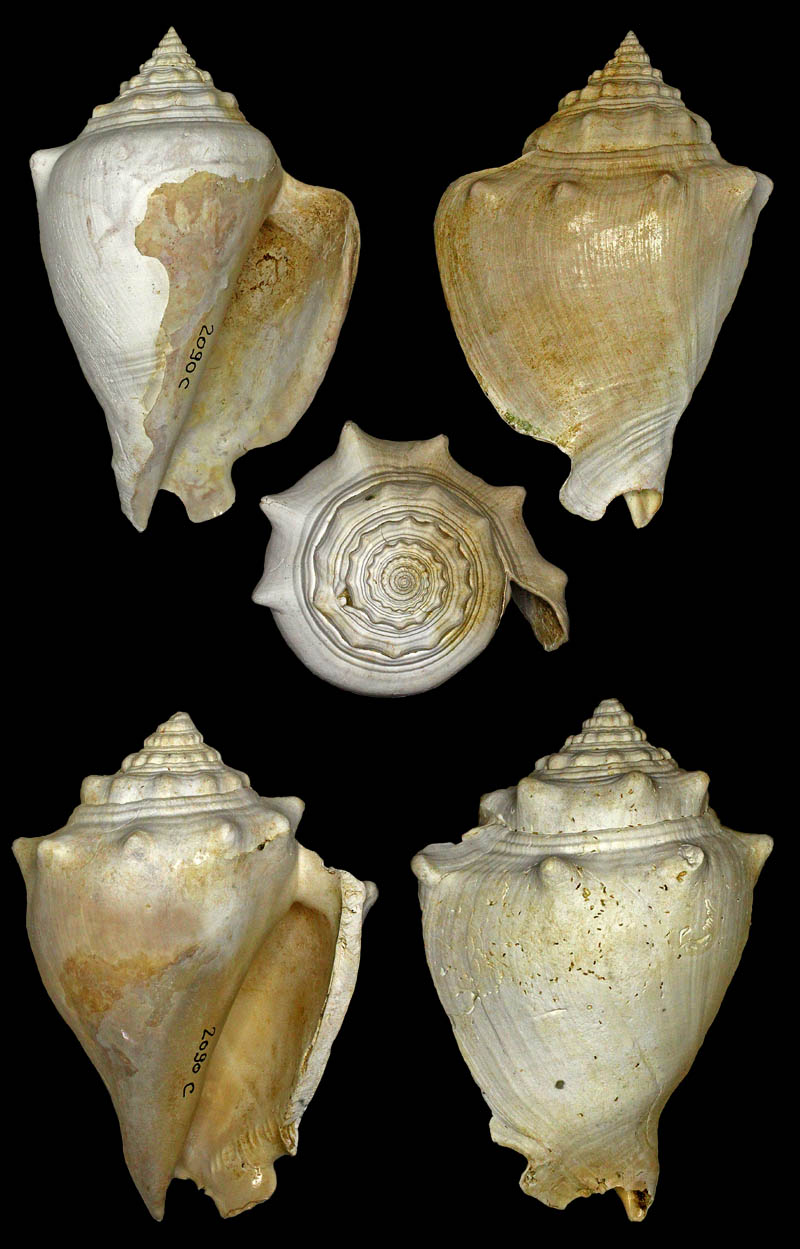
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Pleistocene, Caloosahatchee River, Port La Belle, Hendry County, Florida, USA; Coll. Antoine Heitz no. 2090 C
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Pleistocene, Caloosahatchee River, Port La Belle, Hendry County, Florida, USA; Coll. Antoine Heitz no. 2090 C
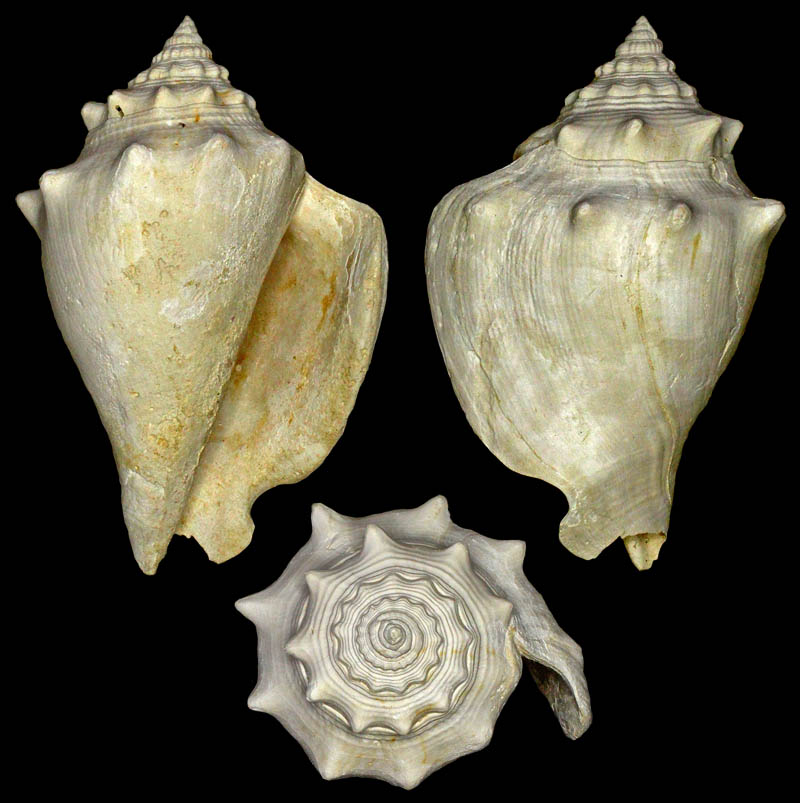
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Pleistocene, New county pit, west of La Belle, Hendry County, Florida, USA; Coll. Antoine Heitz loc. no. HA 28135
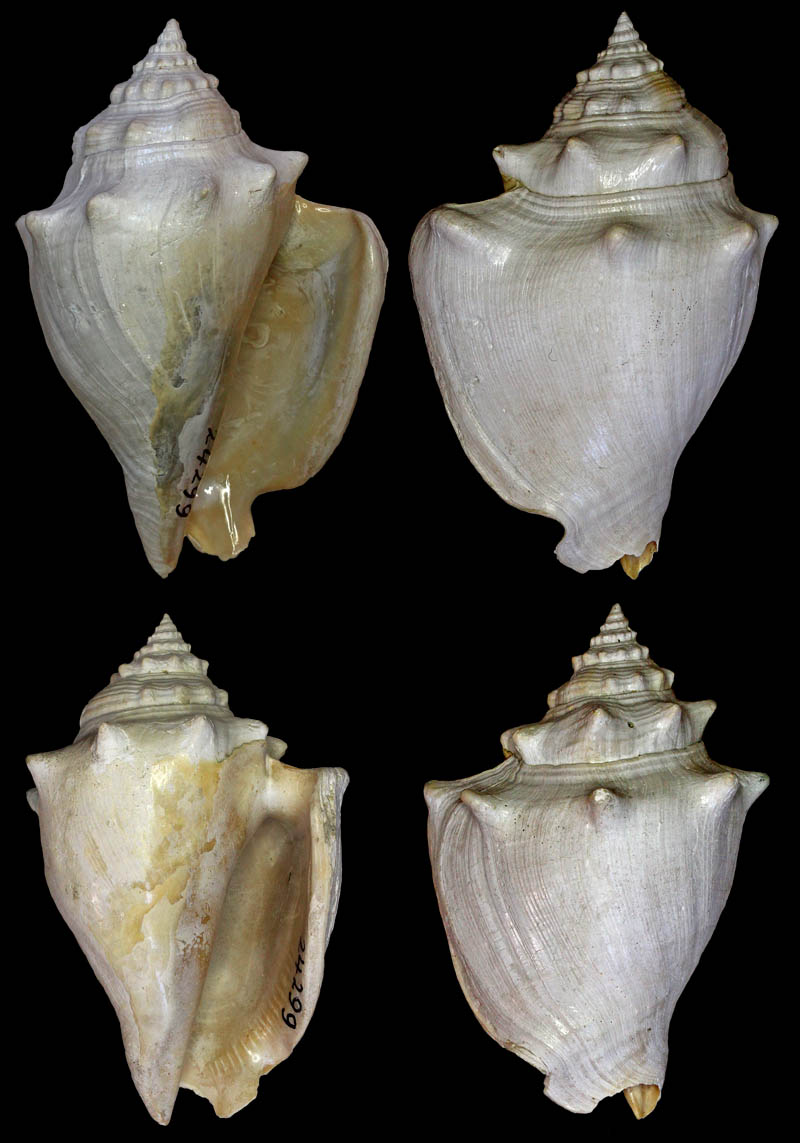
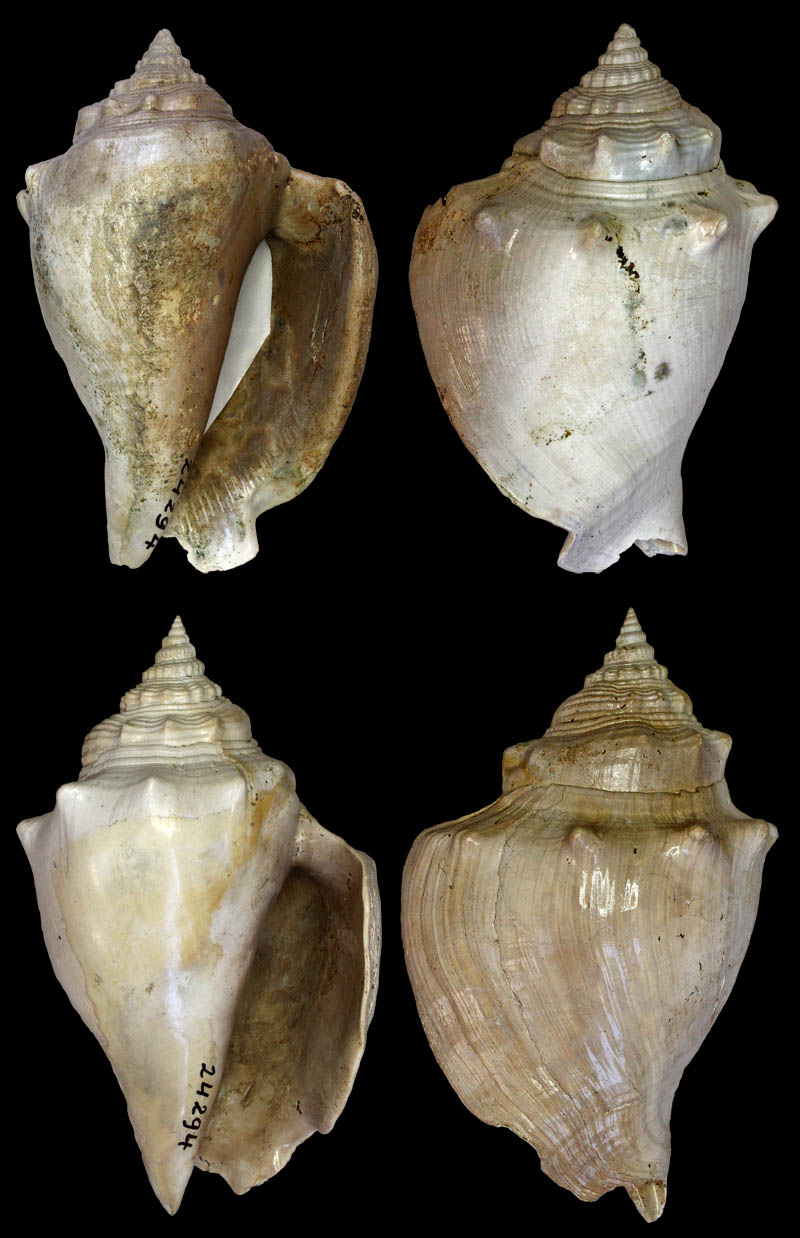
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Bermont Formation, middle Pleistocene; Belle Glade (R441), Palm Beach County, Florida, USA; 1995; Coll. Stichting Schepsel Schelp no. SSS 24299
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Bermont Formation, middle Pleistocene; Hendry County, Florida, USA; 1995; Coll. Stichting Schepsel Schelp no. SSS 24294
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Pliocene; South Bay, Palm Beach County, Florida, USA; 95 mm; Coll. Rupert Hochleitner
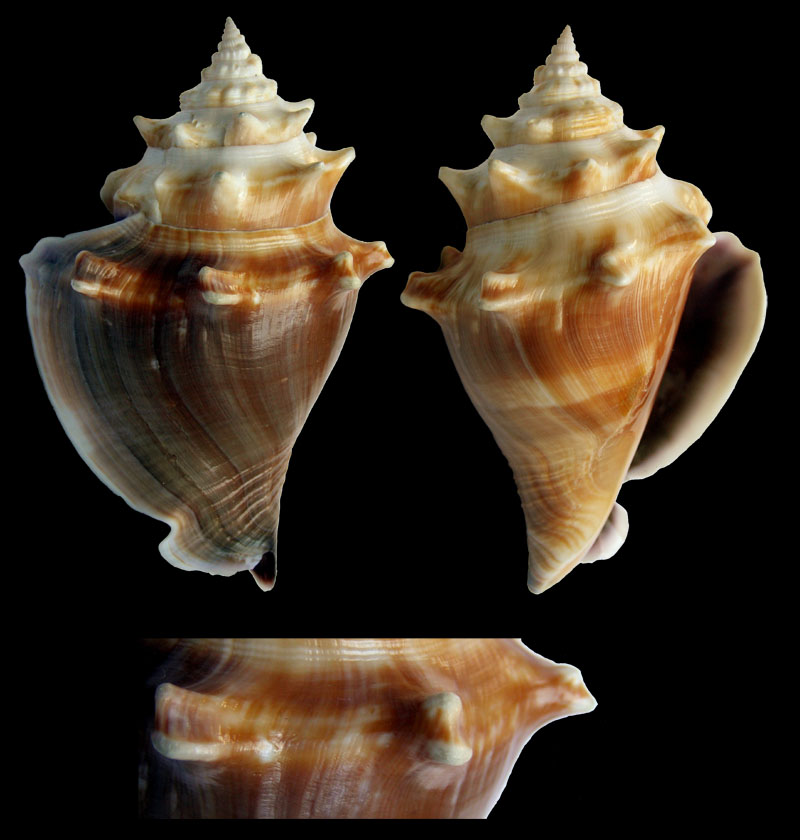
Living specimens
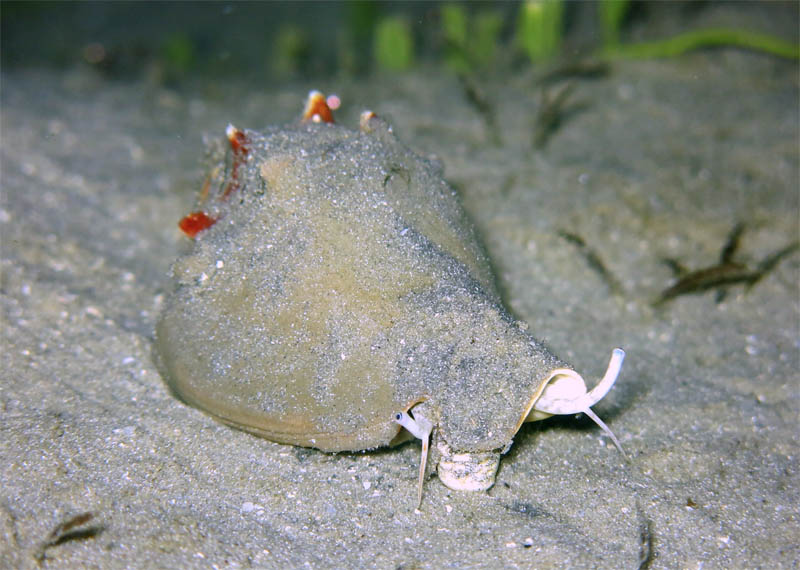
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791; Riviera Beach, Lake Worth Lagoon, Florada, USA, photo & copyright Anton Oleinik
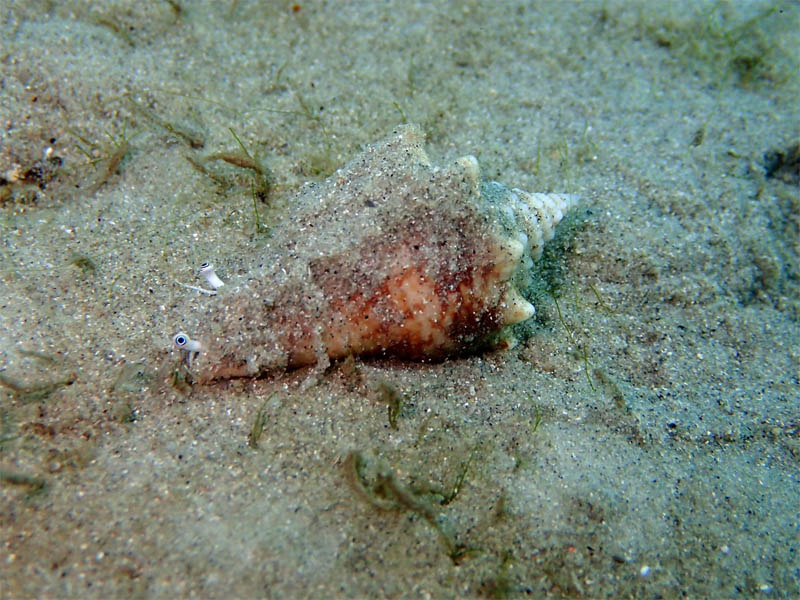
Strombus alatus Gmelin, 1791, juvenile; Riviera Beach, Lake Worth Lagoon, Florada, USA, photo & copyright Anton Oleinik
References
- Abbott, 1954
- Abbott, 1962
- Abbott, 1982
- Abbott, 1986
- Abbott, 1995
- Alcolado, 1983
- Bower, W. J. (1945). Egg laying process of Strombus pugilis alatus Gmelin. The Nautilus 59 (1), 35.
- Brayfield1986
- Bürger, 1995
- Clench & Abbott, 1941
- CoBabe & Ptak, 1999
- Colton, H. S. (1905). Sexual dimorphism in Strombus pugilis. Nautilus, vol. 18, 138-140.
- Coomanns, 1989
- D'Asaro, C. N. (1986). Egg capsules of eleven marine prosobranchs from northwest Florida. Bulletin of Marine Science, 39(1), 76-91.
- DIETL, G. P. (2005, October). Hybridization and adaptive evolution in Plio-Pleistocene strombid snails from Florida. In 2005 Salt Lake City Annual Meeting.
- Gillette, P. & A. Shawl, 2006. Effects of Diet and Sex Ratio on the Reproductive Output of the Florida fighting conch, Strombus alatus. Proceedings of the 57. ANNUAL Gulf and Caribbean Fisheries Institute:57, 947-954.
- Goodrich, C. (1944). Variations in Strombus pugilis alatus. Occasional Papers of the Museum of Zoology, University of Michigan, no. 490, 1-10, fulltext
- Hargreave, D. (1995). An ontogenetic approach to understanding changes in shell morphology over time: the Strombus alatus complex in the Plio-Pleistocene of southern Florida. Tulane Studies in Geology and Paleontology, 27(1-4), 1-52.
- Kosloski, M. E. (2008, October). Are museum collections adequate to test the escalation hypothesis?: A preliminary case study using the Plio-Pleistocene Strombus alatus species complex from Florida. In 2008 Joint Meeting of The Geological Society of America, Soil Science Society of America, American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, Gulf Coast Association of Geological Societies with the Gulf Coast Section of SEPM.
- Merz, R. A. (1979). A study of the behavioral and biomechanical defenses of Strombus alatus, the Florida fighting conch. Master's thesis. University of Florida, Gainesville.
- Mitton, J. B., Berg, C. J., & Orr, K. S. (1989). Population structure, larval dispersal, and gene flow in the queen conch, Strombus gigas, of the Caribbean. The Biological Bulletin, 177(3), 356-362.
- Rowett, C.L. (1957). “A Quaternary Molluscan Assemblage from Orleans Parish, Louisiana.” Transactions of the Gulf Coast Association of Geological Sciences, 7, 153-164.
- Sandford, F. (2003). Population dynamics and epibiont associations of hermit crabs (Crustacea: Decapoda: Paguroidea) on Dog Island, Florida. Memoirs of Museum Victoria, 60(1), 45-52.
- Shawl, A. L., & Davis, M. (2004). Captive breeding behavior of four Strombidae conch. Journal of Shellfish Research, 23(1), 157-164.
- Shawl, A. & A. Spring. 2003. Culturing the Florida fighting conch Strombus alatus. Tropical Fish Hobbyist L1 5:94-97.
- Shelton, D. N. (1997). A systematic list of mollusks in the northern Gulf of Mexico off the Coast of Alabama. Alabama Malacological Research Center: Mobile, AL, USA.)[Copy deposited in molluscan library at AMNH.].
- Thiriot-Quievreux, C. (1983). Summer meroplanktonic prosobranch larvae occurring off Beaufort, North Carolina. Estuaries, 6(4), 387-398.